FIG. 8.
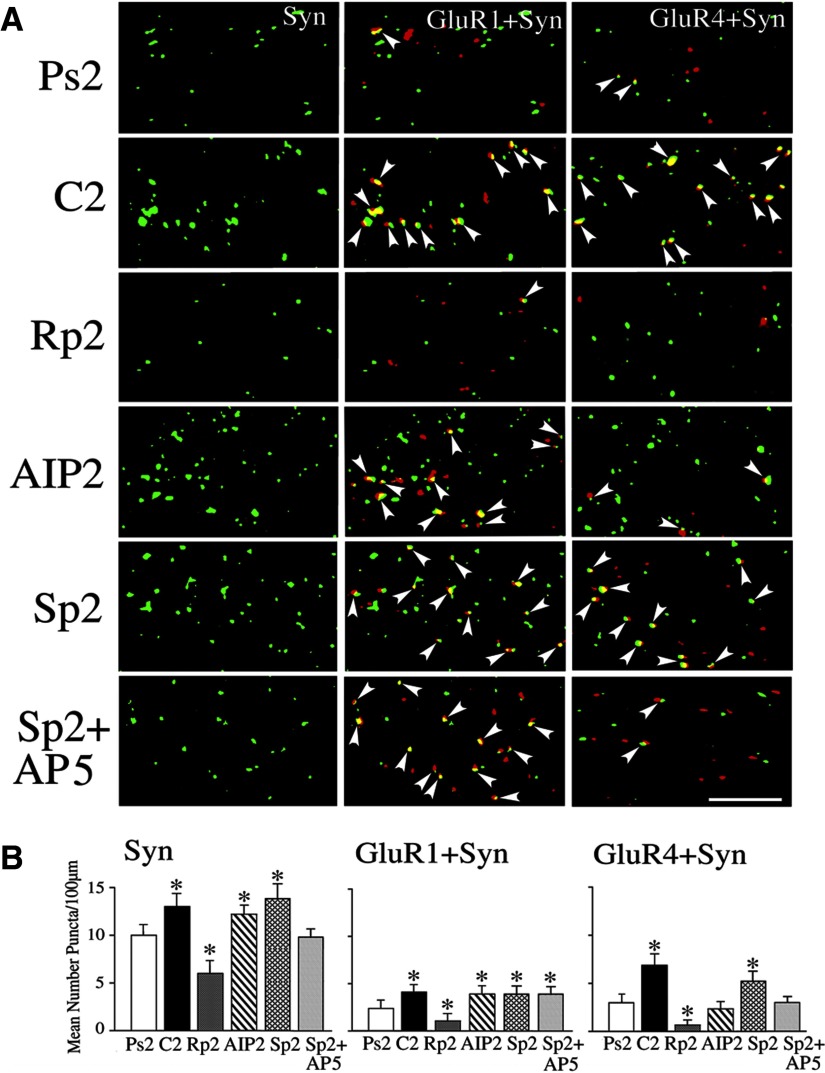
Synaptic incorporation of glutamate receptor 1 (GluR1)- and GluR4-containing α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptors (AMPARs) is dependent on PKA, whereas GluR4 incorporation also requires CaMKII. A: confocal images of selected abducens motor neurons from the different experimental groups show punctate staining for synaptophysin (Syn) and colocalization of GluR1 (GluR1 + Syn) and GluR4 AMPAR subunits (GluR4 + Syn) with synaptophysin. Colocalization of AMPARs (red) with Syn (green) is defined by overlapping (yellow) or adjacent puncta and are indicated by the arrowheads. B: quantitative analysis of Syn, GluR1 + Syn, and GluR4 + Syn punctate staining for the different experimental groups is plotted. Preparations conditioned for 2 pairing sessions (C2) showed significantly greater punctate staining for Syn, GluR1 + Syn, and GluR4 + Syn compared with the pseudoconditioned group (Ps2). Treatment with the PKA inhibitor Rp-cAMPs for 2 sessions (Rp2) significantly reduced the conditioning-related increase in synaptophysin and the colocalization of GluR1 and GluR4 with synaptophysin. Application of the CaMKII blocker AIP for 2 sessions (AIP2) did not affect elevated levels of Syn or GluR1 + Syn, but significantly attenuated GluR4 + Syn. Application of the PKA activator Sp-cAMPs (Sp2) increased punctate staining for synaptophysin and induced synaptic incorporation of GluR1 and GluR4 subunits. Coapplication of Sp-cAMPs with d,l-AP5 (Sp2 + d,l-AP5) for 2 sessions had no effect on GluR1 synaptic insertion but significantly attenuated GluR4. *Indicates significant differences from Ps2. Scale bar = 2 μm.