FIG. 7.
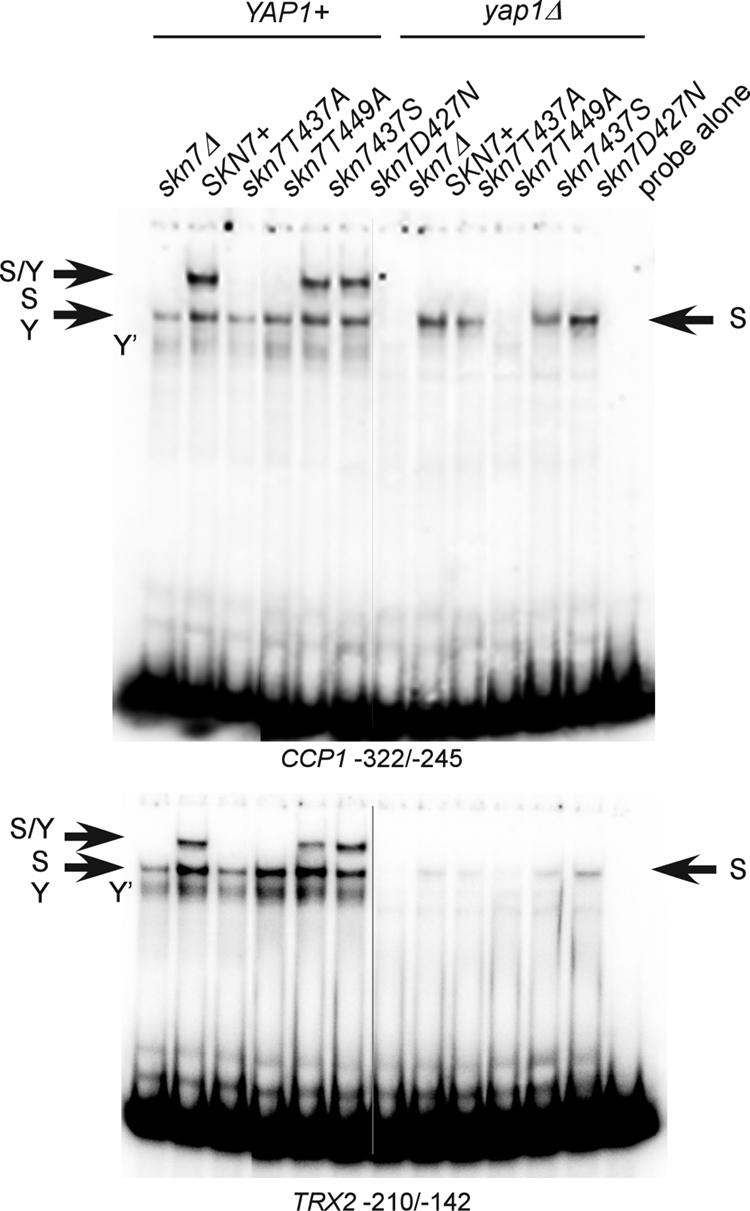
Effect of SKN7 receiver domain mutations on Skn7-Yap1 complex formation. Shown are electrophoretic mobility shift assays in which protein extracts were prepared from a YAP1 skn7Δ (JF1904) or yap1Δ skn7Δ (JF2312) yeast strain carrying wild-type or mutant derivatives of SKN7 and incubated with labeled DNA probes as indicated. Complexes were separated by nondenaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis at 200 V. The CCP1 and TRX2 promoter fragments (−322 to −245 and −210 to −142, respectively) used as probes each contain both Skn7 and Yap1 binding sites. S/Y, complex dependent on both Skn7 and Yap1; S, complex dependent on Skn7; Y, complex dependent on Yap1; Y′, minor complex dependent on Yap1. The S and Y complexes from YAP1+ extracts tend to comigrate. Plasmids carrying SKN7 alleles were the following: SKN7+, pXH1853; skn7-T437A, pXH1854; skn7-T455A, pXH1855; skn7-T449A, pXH1856; skn7-T437S, pXH1857; and skn7-D427N, pXH1858.
