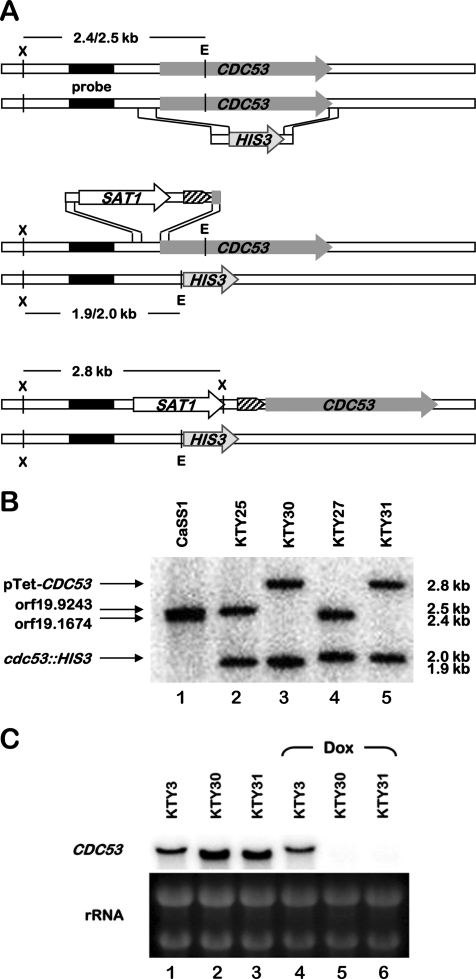
FIG. 1.
Creation of a conditional CDC53 mutant strain. (A) For the creation of heterozygote mutant strains, one allele of CDC53 of wild-type C. albicans strain CaSS1 was replaced by the HIS3 marker (top panel). The SAT1 dominant selectable marker was used to replace the endogenous CDC53 promoter of the remaining wild-type allele by a repressible tetracycline promoter (block arrow with diagonal pattern) (middle panel). The two alleles of the resulting strain are depicted in the bottom panel. The probe used for Southern blot analysis is indicated (filled rectangle) as well as the expected restriction fragment lengths for the different alleles. E, EcoRV; X, XbaI. (B) Southern blot analysis of the parental strain CaSS1 and the mutants KTY25 (cdc53Δ::HIS3/CDC53), KTY30 (cdc53Δ::HIS3/pTet-CDC53), KTY27 (CDC53/cdc53Δ::HIS3), and KTY31 (pTet-CDC53/cdc53Δ::HIS3) using the restriction enzymes and probe shown in panel A. The different alleles and the sizes of the corresponding restriction fragments are indicated at the left and the right sides of the figure, respectively. (C) Northern blot analysis of the control strain KTY3 and the mutants KTY30 and KTY31 after 12 h of growth at 37°C in YPD in the absence or presence of 20 μg of doxycycline/ml (Dox). rRNAs were used as loading controls.