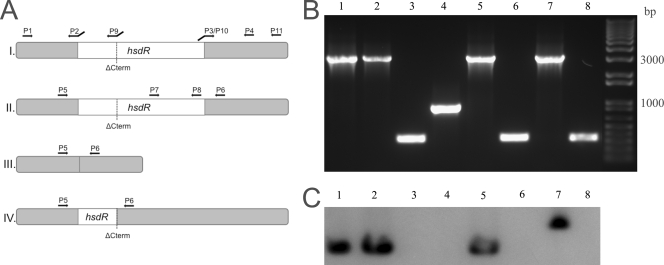
FIG. 1.
Genetic characterization of hsdR mutants. The strains used were RN4220 (lane 1), NCTC8325-4 (lane 2), NCTC8325-4ΔHsdR (lane 3), NCTC8325-4ΔC-term HsdR (lane 4), SH1000 (lane 5), SH1000ΔHsdR (lane 6), COL (lane 7), and COLΔHsdR (lane 8). (A) Localization of primers used to construct hsdR mutants (panel I) (see Materials and Methods for details); of primers used to characterize the hsdR mutants by PCR for wild-type strains RN4220, NCTC8325-4, SH1000, and COL (panel II), for hsdR null mutants NCTC8325-4ΔHsdR, SH1000ΔHsdR, and COLΔHsdR (panel III), and for strain NCTC8325-4ΔC-term HsdR, which contains a truncated version of the hsdR gene (panel IV); and of primers HsdRP7 and HsdRP8 used to amplify the hsdR probe used for Southern blotting (panel II). (B) PCR fragments obtained by amplifying the DNA of the eight strains indicated above using primers HsdRP5 and HsdRP6, which flank the hsdR gene. (C) Results of Southern blot hybridization of SmaI-restricted genomic DNA of the eight strains indicated above with an internal probe for the hsdR gene amplified using primers HsdRP7 and HsdRP8, showing that this gene is absent from the hsdR mutant strains. Note that the probe hybridized with the DNA fragment which was deleted in strain NCTC8325-4ΔC-term HsdR.