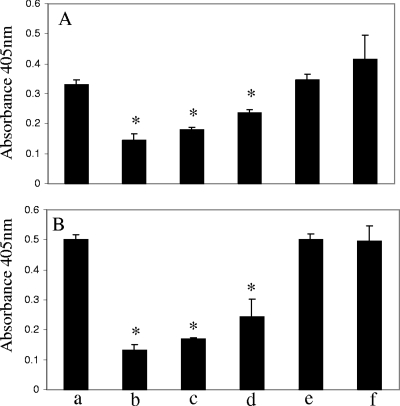
FIG. 1.
Plasminogen and plasmin binding to the surface of A. hydrophila SSU. The log phase and PBS-washed A. hydrophila SSU cells were first incubated with 4 μg of either plasminogen (A) or plasmin (B). After washing away the unbound plasminogen/plasmin, we converted the surface-bound plasminogen to the active form plasmin by tPA and measured the plasmin activity by adding the plasmin-specific chromogenic substrate S-2251. The reaction mixtures that contained only bacterial cells without plasminogen and plasmin served as negative controls and were set as blanks when the absorbance at 405 nm was recorded. Columns a, bacterial cells incubated with plasminogen (A) or plasmin (B); columns b, addition of 2 mM EACA to the binding reaction mixture; columns c and d, addition of 0.125 mg/ml and 0.025 mg/ml, respectively, of the purified IgGs from enolase-immunized mouse serum; columns e and f; addition of 0.125 mg/ml and 0.025 mg/ml, respectively, of purified IgGs from preimmune mouse serum. The asterisk denotes statistically significant differences (P < 0.05) compared to columns a by a Student's t test.