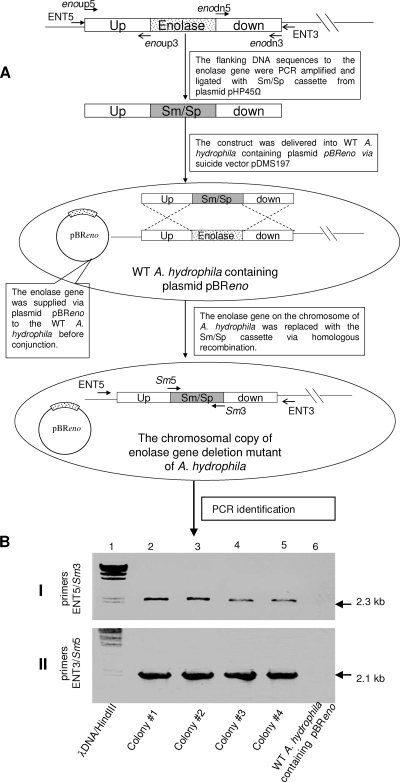
FIG. 7.
Construction of the chromosomal enolase gene deletion mutant of A. hydrophila SSU. (A) The flow diagram showing construction of the mutant. The primer pairs enoup5/enoup3 and enodn5/enodn3 (Table 2) were used to PCR amplify the flanking DNA fragments (open boxes) to the enolase gene (dotted box). The Sm/Sp gene cassette was removed from the plasmid pHP45Ω. The suicide vector pDMS197 was used for delivering the construct into WT A. hydrophila that contained an additional copy of the enolase gene on the plasmid pBReno. By homologous recombination, the enolase gene on the chromosome of A. hydrophila was replaced with the Sm/Sp cassette. The arrows represent the direction and position of different primers. (The figure is not drawn to scale). (B) PCR identification of the potential enolase gene deletion mutants of A. hydrophila. In the experiment shown in panel I, the primer set ENT5/Sm3 was used while primer set ENT3/Sm5 was employed for the experiment shown in panel II. Lanes 2 to 5, potential enolase mutant colonies. Other lanes are as indicated.