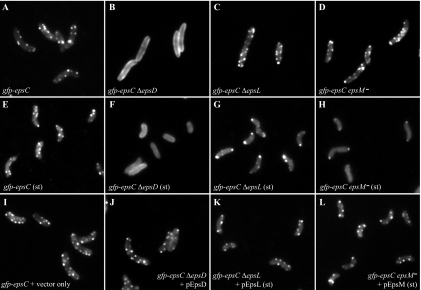
FIG. 6.
Differential localization of GFP-EpsC in the absence of EpsD, EpsL and EpsM. Localization of chromosomally expressed GFP-EpsC was examined in ΔepsD (B and F), ΔepsL (C and G), and epsM mutant (D and H) backgrounds in log- and stationary-phase (st) cultures and compared with its localization in an otherwise wild-type background (A and E) by fluorescence microscopy. GFP-EpsC displayed a continuous membrane localization in the gfp-epsC ΔepsD strain (B) compared to the otherwise wild-type background (A). Punctate fluorescence was restored when the gfp-epsC ΔepsD strain was complemented with the pEpsD plasmid in the presence of 10 μM IPTG (J). Both the gfp-epsC ΔepsL strain (C) and gfp-epsC epsM mutant (D) retained punctate fluorescence, with subtle accumulation at the polar membrane. In stationary-phase cultures, this phenotype appeared to be magnified, as there is a distinct accumulation at the poles in both the gfp-epsC ΔepsL strain (G) and gfp-epsC epsM mutant (H). Introduction of the pEpsL and pEpsM plasmids to the epsC ΔepsL strain (K) and gfp-epsC epsM mutant (L), respectively, restored the patterns to that of the wild-type strain containing a vector control in the stationary-phase cultures (I).