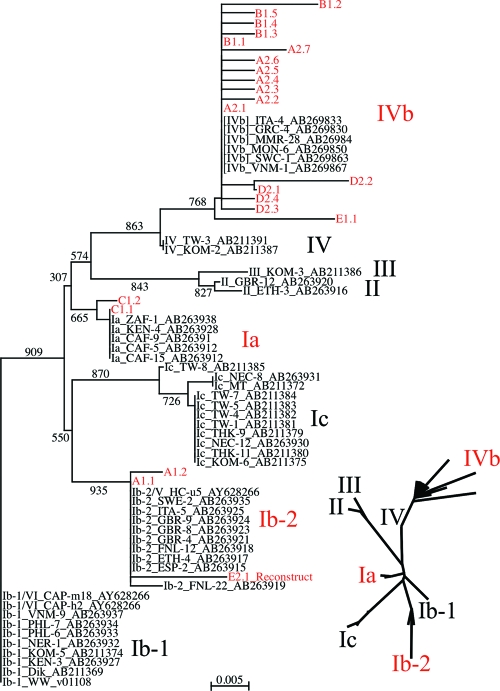
FIG. 3.
Genotyping of Israeli BKV isolates from RT patients on the basis of their archetype NCRR sequences. To form the tree, nonarchetype NCRR sequences were excised in silico from the complete BKV sequences of all isolates, and when necessary, the archetype was reconstructed (see the supplemental material for details). Six additional complete BKV sequences were downloaded from the EMBL database. All archetype NCRR sequences were aligned, the data set was bootstrapped 1,000 times, and a nearest-neighbor phylogenetic tree was generated with the ClustalX program. The tree was visualized by using the njplot program (large image at the bottom right). The WW NCRR sequence was used as the reference outgroup. An unrooted tree was also visualized by using the unrooted program (inserts at the bottom right). For visual clarity, only the names of the genotypes and subgenotypes appear for the unrooted tree. Isolates are designated by their genotype and subgentoype, as described by Zheng et al., (49); the isolate name; and then the EMBL accession number. Israeli archetype isolates are designated by a letter to indicate the patient; the number 1 or 2 to indicate whether the isolate was WWL1 or WWL2, respectively; a period; and a number to indicate the snvNCRR variant. The name subgenotype IVb has been introduced to describe the new subgroup of genotype IV, assuming that the original genotype IV will be renamed IVa.