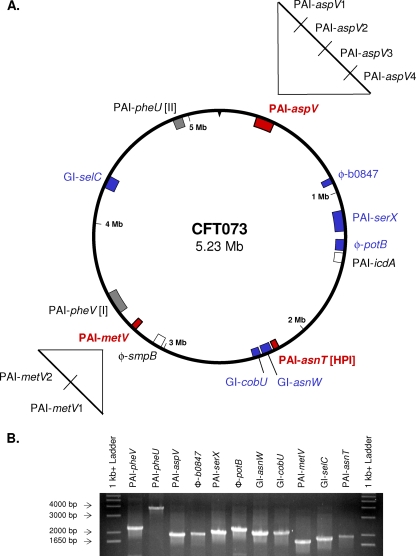
FIG. 1.
(A) Thirteen genomic islands of >30 kb in E. coli CFT073. Isogenic mutants were constructed in 11 GIs (shaded) using the lambda red recombinase system. Deletion mutants of nine of these mutants (shaded blue and red) were tested in cochallenge with wild-type strain CFT073 in the CBA/J mouse model of ascending UTI. Deletion mutants of six islands shown in blue did not show levels of colonization that were statistically different from that of CFT073. Mutants with deletion of genes in the three islands shown in red (PAI-aspV, PAI-metV, and PAI-asnT) were significantly outcompeted by wild-type strain CFT073 in the bladders and/or kidneys (P < 0.05). Smaller deletion mutants spanning PAI-aspV (PAI-aspV1, PAI-aspV2, PAI-aspV3, and PAI-aspV4) and PAI-metV (PAI-metV1 and PAI-metV2) were also constructed and tested in cochallenge with strain CFT073. Isogenic mutants in GIs PAI-icdA and PAI-smpB were not created (white). (B) Confirmation of homologous recombination and subsequent replacement of each GI with a kanamycin resistance cassette. PCR amplification of isogenic mutants with primers flanking the targeted GIs (32 to 123 kb) resulted in PCR products with the predicted sizes: ΔPAI-pheV (2,204 bp), ΔPAI-pheU (3,820 bp), ΔPAI-aspV (1,883 bp), φΔ-b0847 (1,938 bp), ΔPAI-serX (2,061 bp), φΔ-potB (2,290 bp), ΔGI-asnW (2,113 bp), ΔGI-cobU (2,122 bp), ΔPAI-metV (1,746 bp), ΔGI-selC (1,850 bp), and ΔPAI-asnT (1,943 bp). The estimated sizes of PCR products were consistent with the predicted sizes.