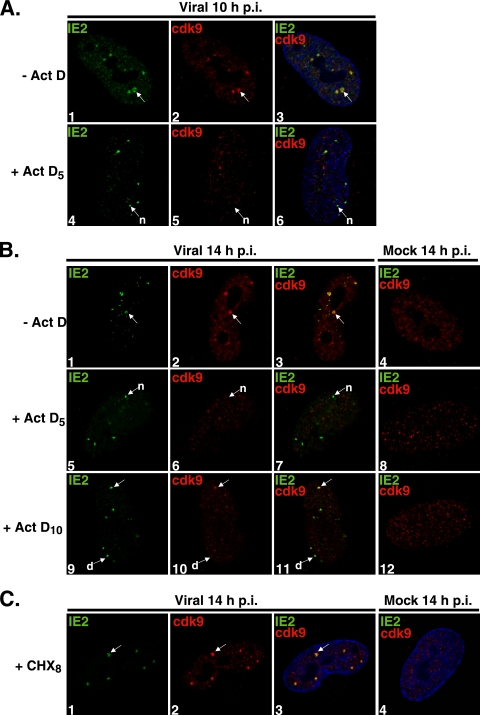
FIG. 2.
Cdk9 localization at the viral transcriptosomes requires active transcription. G0-synchronized cells were released into G1 and seeded onto glass coverslips. One hour later, cells were infected with HCMV Towne (MOI of 5) or with mock infection supernatant. (A) At 5 h p.i., Act D (10 μg/ml) (+ Act D5) or control medium (− Act D) was added; at 10 h p.i., cells were fixed for IFA. (B) Act D or control medium (− Act D) was added at 5 h p.i. (+ Act D5) or at 10 h p.i. (+ Act D10), and cells were fixed at 14 h p.i. for IFA. (C) At 8 h p.i., cells were treated with CHX (100 μg/ml) (+ CHX8) or control medium; cells were fixed at 14 h p.i. for IFA. Cells were stained with antibodies specific for IE2 and cdk9, followed by fluorescein isothiocyanate- and Cy3-conjugated isotype-specific secondary antibodies. Nuclei were stained with Hoechst dye. The white arrows marked “n” indicate viral transcriptosomes that do not show colocalization between stained proteins, the arrows marked “d” show decreased cdk9 staining at viral transcriptosomes, and the unmarked white arrows point to examples of colocalization. All of the images represent confocal optical 0.2-μm sections at a magnification of ×1,000 under conditions of oil immersion.