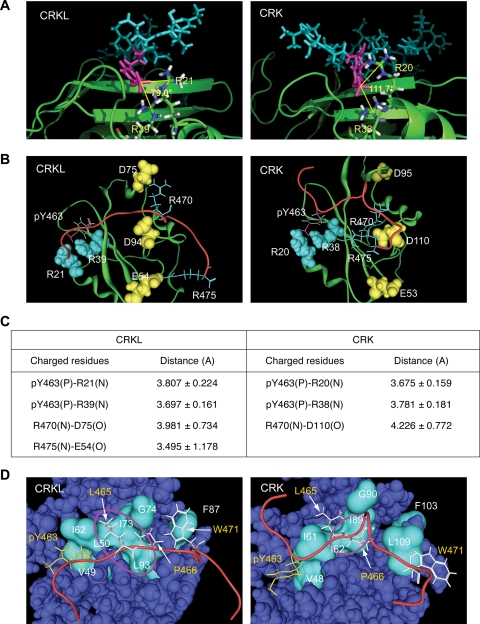
FIG. 2.
Structural basis of interaction between CRKL SH2 domain and pY peptide. (Structural information is available in the supplemental material.) (A) Electrostatic interaction between pY463 in the peptide sequence and two arginine residues in the SH2 domain. pY463 is shown in magenta. SH2 domains are shown in ribbon representations in green, except that two arginine residues interacting with the phosphotyrosine are shown in a stick model. The number shown between the two lines is the angle formed by the central carbon atom in the guanidinium group in the two arginine residues and the phosphorus atom in the phosphate group in pY463 to illustrate qualitative differences in the way that CRKL and CRK SH2 domains interact with the phosphotyrosine in the peptide. (B) Interaction of charged residues between the SH2 domain and FGFR1 peptide sequence. The SH2 domain of CRK and CRKL are colored in green in a ribbon representation. The backbone of the phosphorylated Y463 peptide sequence is shown in red. Charged residues in the peptide sequence and SH2 domain are shown in stick or space fill models, respectively. The phosphate group in pY463 is shown in red. Negatively and positively charged amino acids are shown in yellow or light blue, respectively. (C) Summary table for the distance between two atoms involved in electrostatic interactions. (D) Hydrophobic interactions between the SH2 domain and FGFR1 peptide sequence. The backbone of the pY peptide is shown in red. Hydrophobic residues in the peptide sequence are shown in stick models; pY463 in yellow and the others in white. Hydrophobic residues along the peptide binding area in the SH2 domain are shown in cyan in the surface model. Hydrophobic pockets are highlighted by a circle in magenta.