FIG. 1.
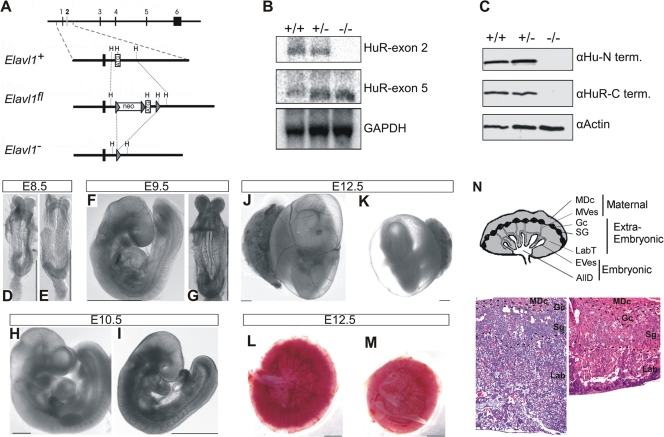
Midgestational phenotype of HuR-deficient embryos. (A) Schematic of the complete exon/intron orientation of the Elavl1 locus on mouse chromosome 8 and magnifications of the region containing the second exon (white box) as a wild-type (Elavl1+), targeted (Elavl1fl), and inactive, Cre-recombined locus (Elavl1−). The neo selection gene and loxP genes (arrowheads) are indicated. Restriction sites for HindIII (H) are also shown for alignment. (B) Northern analysis of RNA extracts from Elavl1+/+ (+/+), Elavl1+/− (+/−), and Elavl1−/− (−/−) MEFs with specific probes for exons 2 and 5, indicating the presence of shorter mHuR transcripts lacking exon 2. The Gapdh mRNA is shown for quantitation. (C) Western blotting of protein extracts from E11.5 Elavl1+/+ (+/+), Elavl1+/− (+/−), and Elavl1−/− (−/−) embryos with antibodies against the amino (3A2) and carboxy (T17) termini of mHuR depicting its complete absence. Actin is shown as a loading control. (D to K) Representative stereophotographs of staged Elavl1+/+ (D, F, H, and J) and Elavl1−/− (E, G, I, and K) embryos and conceptuses, indicating the stage retardation phenotype of the latter and the diminished blood flow in the corresponding yolk sacs. The mutant phenotype correlates with smaller placentas (M) as opposed to control placentas (L). Size bars correspond to 1 mm. (N) Diagram of placental compartments and representative hematoxylin/eosin histology of E12.5 placentas from control (+/+) and mutant (−/−) conceptuses. Dotted lines indicate the maternal decidua, giant cell, spongiotrophoblast, and labyrinth layers. Magnification, ×100. MDc, maternal decidua; MVes, maternal vessels; Gc, giant cells; Sg, spongiotrophoblasts; Lab, labyrinth; LabT, labyrinthine trophoblasts; EVes, embryonic vessels; AllD, nonendothelial allantoic derivatives.