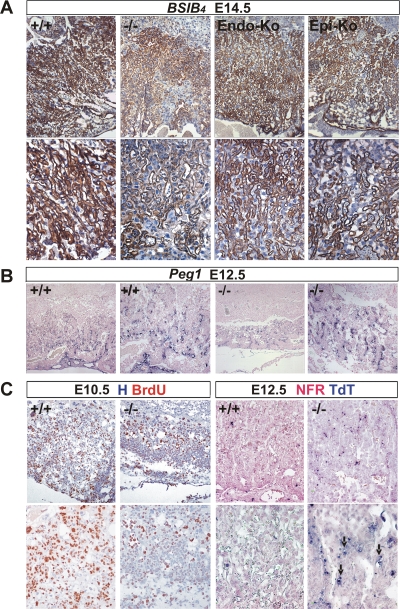
FIG. 5.
Abnormal labyrinth branching extension, vascularization, proliferation, and apoptosis in mature HuR-deficient placentas. (A) Immunohistochemical detection of isolectin B4 (brown staining) in E14.5 placentas from Elavl1+/+ (+/+), Elavl1−/− (−/−), Tie1 Cre Elavl1fl/fl (Endo-Ko), and Sox2 Cre Elavl1−/− (Epi-Ko) conceptuses revealing the matrix between the endothelium of the fetal vessels and the labyrinth trophoblast of the maternal lacunas. The counterstain was hematoxylin. Magnification, ×100 (top panels) and ×200 (bottom panels). (B) In situ detection of Peg1 mRNA (blue) in E12.5 placentas from Elavl1+/+ (+/+) and Elavl1−/− (−/−) conceptuses, marking placental endothelia. Magnification, from the left, ×100 for the first and third panels and ×200 for the second and fourth panels. Note the reduction in the area of the labyrinth endothelia in the mutant placentas. (C) Left panels, immunohistochemical detection of BrdU incorporation (brown) in E10.5 chorioallantoic placentas from Elavl1+/+ (+/+) and Elavl1−/− (−/−) conceptuses showing reduced proliferation in the mutant labyrinth layers. The counterstain was hematoxylin (H). Magnification, ×100 (top panels) and ×200 (bottom panels). Right panels, TUNEL detection of apoptotic cells (TdT; blue) in E12.5 placentas from Elavl1+/+ (+/+) and Elavl1−/− (−/−) conceptuses. Arrows indicate apoptotic trophoblastic cells. The counterstain was nuclear fast red (NFR). Magnification, ×100 (top panels) and ×200 (bottom panels).