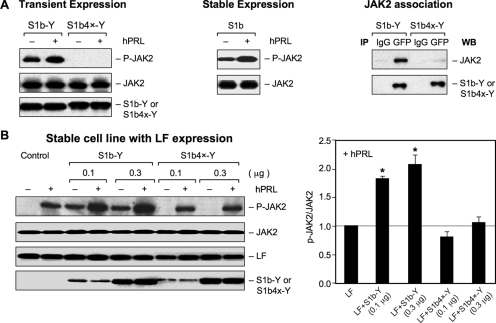
FIG. 3.
Effect of the Cys mutation on JAK2 phosphorylation. (A) (Left) HEK293 cells were cotransfected with wild-type S1b-Y or S1b4x-Y (0.2 μg) with JAK2 (0.2 μg) and incubated in the presence (+) or absence (−) of hPRL (150 ng/ml) for 0.5 h. (Middle) JAK2 phosphorylation in HEK293 cells stably expressing S1b transfected with JAK-2 and incubated in the presence or absence of hPRL. (Right) Co-IP analysis of JAK2 association with S1b wild type and the Cys mutant. (B) (Left) HEK293 cells stably expressing LF were transiently cotransfected with JAK2 (0.2 μg) with different doses of S1b wild-type or S1b4x-Y constructs and incubated in the presence or absence of hPRL (150 ng/ml) for 0.5 h. (Right) Levels of JAK2 phosphorylation stimulated by hPRL from three independent experiments were quantified and normalized by transiently expressed JAK2. The values (mean plus standard error) are presented relative to LFs (1; horizontal line). *, P < 0.05. S1b4x-Y, Cys-to-Ser mutation at aa 36, 46, 75, and 86 of the wild-type SF S1b (S1b-Y). Cell extracts were analyzed by Western blot analysis using anti-phospho-JAK2 (p-JAK2) for JAK2 phosphorylation and anti-JAK2 for transfected JAK2 expression. Anti-PRLR (H300) antibody was used for endogenous LF expression and anti-GFP for expression of transfected S1b-Y and S1b4x-Y.