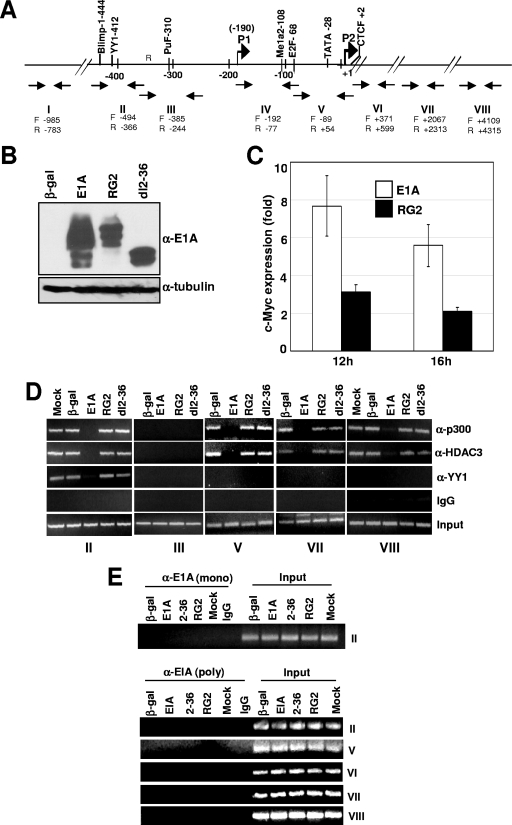
FIG. 1.
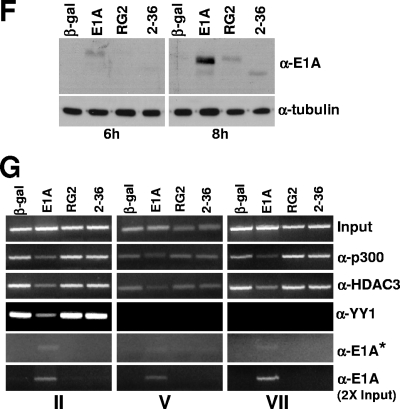
E1A interferes in the recruitment of YY1, p300, and HDAC3 to the Myc promoter and the coding regions. (A) Location of the upstream YY1 binding site on the human c-Myc promoter in relation to the major P2 promoter transcriptional start site and the primer pairs used for ChIP assays. P1 and P2 are the minor and major transcriptional initiation sites, respectively. (B) Expression of the WT and mutant E1A proteins in virus-infected cells. MCF10A cells were serum starved for 32 h and then infected with Ad variants for 16 h, and the cell lysates were subjected to Western immunoblotting using anti-E1A monoclonal antibody (M73; a gift of E. Moran). (C) Analysis of Myc RNA in cells infected with control and E1A viruses. Myc RNA was quantified using a real-time PCR assay as described previously (2). (D) Occupancy of p300, YY1, and HDAC3 on the promoter and coding regions of c-Myc in E1A-expressing quiescent cells. Virus-infected MCF10A cells as above were harvested, and the chromatin was subjected to ChIP assays as described under Materials and Methods. Images of the agarose gels showing the PCR-amplified DNA are shown. The antibodies used are anti-p300 (α-p300) (N15), anti-HDAC3 (α-HDAC3) (B-12), anti-YY1 (α-YY1) (H414), and anti-E1A (α-E1A) (13 S-5 and M73) (all antibodies were from Santa Cruz). The experiment was repeated twice with identical results. (E) Lack of association of E1A on the promoter and coding regions of the Myc chromatin in E1A-expressing cells. Experimental details are as for panel D. Anti-E1A monoclonal antibody M73 (gift of E. Moran) and the anti-E1A polyclonal antibody (Sc-430; Santa Cruz) were used to immunoprecipitate the chromatin. (F) Western blot showing expression of WT and mutant E1A proteins at 6 and 8 h after infection of quiescent MCF10A cells with indicated viruses. Details are as for panel B. (G) Association of E1A with chromatin-bound p300 and dissociation of the p300 complex at 8 h postinfection. Chromatin prepared from virus-infected cells was subjected to ChIP assays with antibodies and primer pairs as shown. The asterisk indicates that the gel image in this panel was obtained with double the exposure time used for other panels. The E1A band in the bottom panel could be detected after taking twice the amount of chromatin used for the other panels.