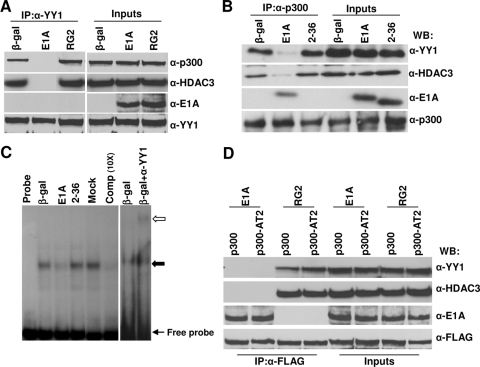
FIG. 5.
Binding of E1A to p300 interferes in ternary complex formation between p300, YY1, and HDAC3 in vivo, and dissociation of the p300 complex by E1A is not dependent on p300 HAT activity. Serum-starved MCF10A cells were infected with viruses expressing WT E1A or the mutant RG2 or dl2-36 protein for 16 h and harvested, and then the cell lysates were immunoprecipitated using antibodies as shown. The immunoprecipitated (IP) proteins were identified by Western immunoblotting using antibodies as indicated. α-p300, anti-p300; α-HDAC3, anti-HDAC3; α-E1A, anti-E1A; α-YY1, anti-YY1; β-gal, beta-galactosidase. (A) Cell extracts equivalent to 2 mg of protein were immunoprecipitated with anti-YY1 (H414) antibody, followed by Western immunoblotting (WB) with the anti-YY1 (H-10), anti-HDAC3 (B-12), anti-E1A (M73), and anti p300 (RW128) antibodies. For input lanes, 1/20 of the protein used for immunoprecipitation was loaded directly. (B) Immunoprecipitation using anti-p300 (N15) antibody. Other details are the same as for panel A. (C) EMSA showing the effect of E1A on YY1 binding to the YY1 binding site of the Myc promoter. Nuclear extracts were prepared from serum-starved MCF10A cells infected with Ad variants as shown and incubated with the Myc promoter YY1 binding site in vitro. The DNA-YY1 protein complexes (shown by an arrow) were resolved on a 5% nondenaturing polyacrylamide gel as described in Materials and Methods. For the supershift assay, a reaction mixture was incubated in the presence of an anti-YY1 antibody. The open arrow indicates the supershifted band. (D) Cell extracts prepared from cells coinfected with Adp300AT2 (see Materials and Methods) and E1A variants were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG antibody (catalog no. F7425; Sigma) and Western immunoblotted using antibodies as indicated. α-FLAG, anti-FLAG antibody.