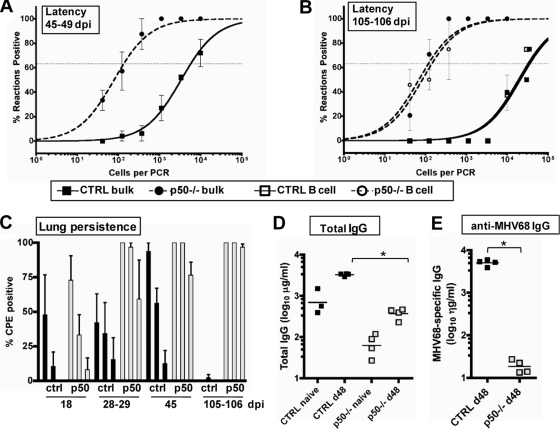
FIG. 4.
Hyperestablishment of splenic latency and persistence in the lungs is associated with a lack of serum IgG against MHV68 in NF-κB1 p50−/− mice. (A) Frequency of splenocytes harboring viral genomes at 45 to 49 dpi. Bulk splenocytes were prepared from two sets of control mice (CTRL, B6 and B6x129PF2/J) or NF-κB1 p50−/− mice (p50−/−, B6 and B6;129P) infected with 100 PFU of WT MHV68. Limiting-dilution viral genome PCR analysis was utilized to determine the frequency of latency for bulk splenocytes from CTRL mice and p50−/− mice at 45 to 49 dpi (1/5,685 and 1/135, respectively). (B) Frequency of splenocytes harboring viral genomes at 105 to 106 dpi. Bulk splenocytes and CD19+ B cells were prepared from control mice (CTRL, B6) or NF-κB1 p50−/− mice (p50−/−, B6) with 100 PFU of WT MHV68. Limiting-dilution viral genome PCR analysis was utilized to determine the frequency of latency for bulk splenocytes from CTRL mice and p50−/− mice at 105 to 106 dpi (1/35,950 and 1/118, respectively) and for B cells (1/32,500 and 1/142, respectively). Postseparation FACS analysis indicated that the mean purities for CD19+ cells were 93% ± 2.1% for CTRL and 91.4% ± 0.1% for p50−/−. Curve fit lines were derived from nonlinear regression analysis, and symbols represent the mean percentage of wells positive for viral DNA ± the standard error of the mean. The dashed line represents 63.2%, from which the frequency of viral genome-positive cells was calculated based on the Poisson distribution. The data shown represent at least two independent experiments with spleen cells pooled from three to five mice per experimental group. (C) Persistence in the lungs. Lung tissue was isolated from three or four infected control mice (CTRL, BL6) or NF-κB1 p50−/− mice (p50−/−, BL6) at the indicated dpi with 100 PFU of WT MHV68. Bars for each sample represent the mean percentage for 16 wells positive for CPE upon plating fourfold dilutions (1:10, 1:40, and 1:160) of mechanically disrupted lung tissue from an individual mouse on an indicator MEF monolayer. (D) Determination of total IgG production in sera of individual naïve versus infected CTRL and p50−/− mice. The bar represents the geometric mean titer. The mean total IgG was significantly different for comparisons of naïve or infected sera within or between CTRL and p50−/− mice (P < 0.006). (E) Determination of MHV68-specific IgG production in sera of individual infected mice. The bar represents the geometric mean titer. Naïve sera from both strains of mice had undetectable levels of MHV68-specific IgG (data not shown). The mean anti-MHV68 IgG titer was significantly different (P < 0.0001).