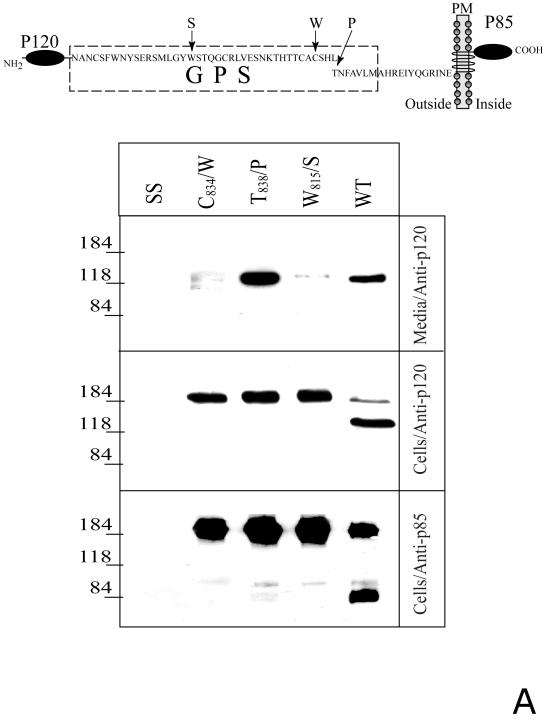
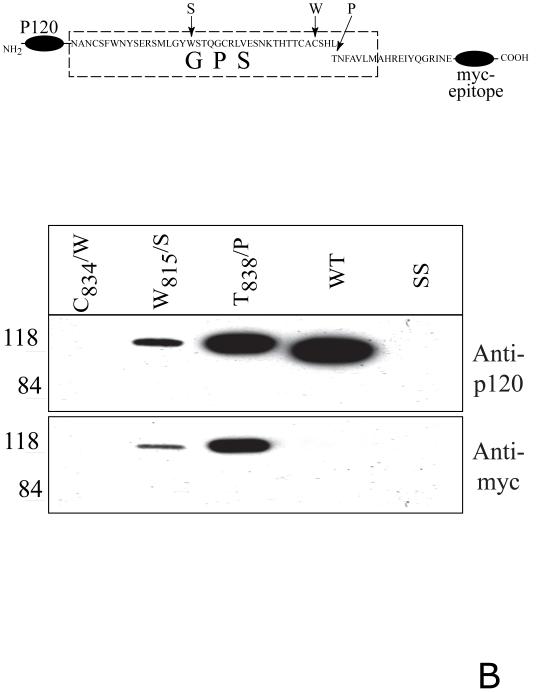
Fig. 2. Proteolytic processing of the full-length and soluble deletion constructs of CIRL mutated in the GPS domain.
A. Soluble forms of CIRL GPS mutants. COS cells were transfected with either wild-type CIRL or its GPS mutants with single residue substitution within the GPS domain (C834/W, W815/S, and T838/P), schematically described at the top panel, PM - plasma membrane. The cells were harvested and analyzed by Western blotting with anti-p120 or anti-p85 antibody. The conditioned media were precipitated with α-latrotoxin-agarose followed by Western blotting with anti-p120 antibody. Salmon sperm DNA transfected cells (SS) were used as control. B. Secretion of soluble GPS mutants of the CIRL ectodomain. COS cells were transfected with the plasmids encoding either the wild type CIRL ectodomain or three single-residue mutant constructs (C834/W, W815/S, and T838/P), schematically described at the top panel. The conditioned media were precipitated with α-latrotoxin-agarose followed by Western blotting with either anti-p120 or anti-myc antibody. Note an increase in the apparent size of p120 in the non-cleaved mutants W815/S, and T838/P due to the 3.8 kDa myc-tag addition. The pictures shown are representative of five independent transfection, precipitation and blotting experiments that produced essentially similar results.