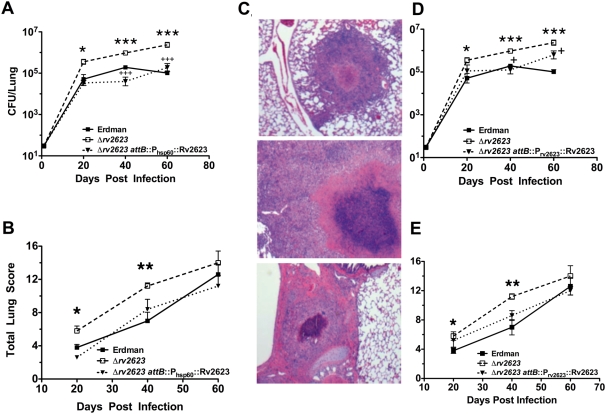
Figure 3. In Vivo growth of and pathology caused by Δrv2623 in guinea pigs.
Outbred Hartley guinea pigs given an aerosol challenge of ∼30 CFU were assessed for pulmonic bacterial burden (A,D) and the severity of lung pathology (B,E). Closed box, open box, and triangle represent guinea pigs infected with Erdman, in (A,B,D,E), Δrv2623, in (A,B,D,E), and Δrv2623 attB::Phsp60 Rv2623, in (A,B), or Δrv2623 attB::Prv2623 Rv2623, in (D,E). Comparing the wildtype Erdman and the Δrv2623 strains: *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001. Comparing the Δrv2623 and the Δrv2623::complemented strains (Δrv2623 attB::Phsp60 Rv2623 or Δrv2623 attB::Prv2623 Rv2623): +++p<0.001; +p<0.05. (C) Hematoxylin & Eosin-stained lung sections (40 days post infection) from guinea pigs infected with Erdman (top), Δrv2623 (middle), and Δrv2623 attB::Phsp60 Rv2623 (bottom) M. tuberculosis. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean.