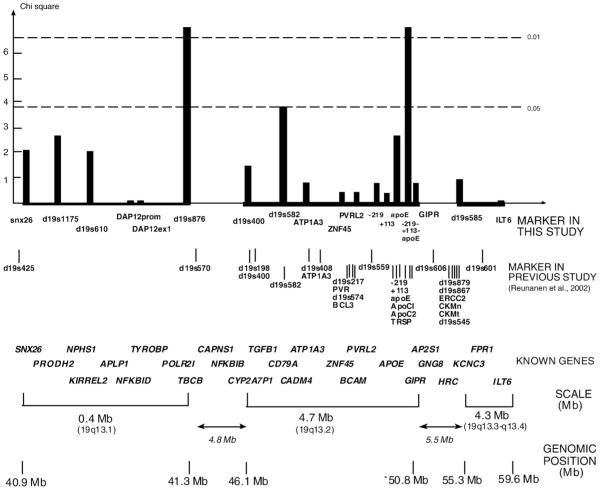
Fig. 1.
Association of chromosome 19q13 markers with MS. The most significant allele-wise (1 df) chi-square values are shown. Known genes of the regions are positioned in the figure as landmarks. The markers were genotyped in 459 MS trio families, except ILT6, GIPR, and ZNF45, which were genotyped in 186 families. Linkage disequilibrium (LD) between pairs of SNP markers was analysed with Haploview program. Lod score ≥3 was used as criterion for significant LD. Microsatellite-microsatellite and microsatellite-SNP LD was analysed by comparing the observed haplotype distribution in fully informative families to the distribution expected on the basis of marker allele frequencies using the χ2 test. The p-value p<0.001 was used as criterion for significant LD. In the 19q13.1 subregion all the markers exhibited significant LD except the markers pairs SNX26/DAP12-StyI and DAP12-StyI/DAP12-HaeIII (data not shown). In the 19q13.2 subregion the APOE SNPs were the only markers that showed significant LD with each other, and 19q13.3-q13.4 subregion markers were not in significant LD (data not shown). There was no LD between the subregions.