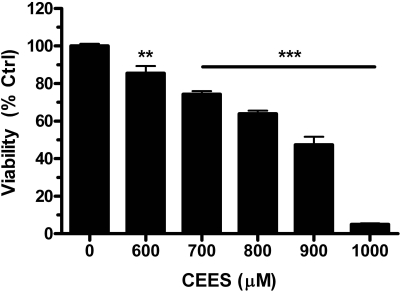
Fig. 2.
CEES exposure causes a concentration-dependent injury of human airway epithelial cells. Human lung 16HBE cells were grown to approximately 90% confluence and treated with concentrations of CEES ranging from 600 to 1000 μM for 24 h. Cell viability decreased in a dose-dependent manner as measured by quantifying calcein AM fluorescence. Data represented as mean ± S.E.M., n = 4 where control group fluorescence was defined as 100% viability.