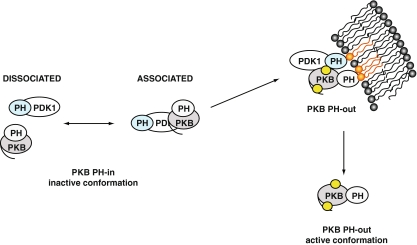
Fig. 3.
Schematic model of the interaction of PKB with PDK1. Prior to stimulation, PKB and PDK1 form a complex in dynamic equilibrium in the cytoplasm. In the PKB inactive conformation, PKB PH and kinase domains interact, noted as “PH-in”. Upon PDGF stimulation, the PKB/PDK1 complex is recruited to the plasma membrane due to interaction with phosphoinositides (in orange). The equilibrium of PKB/PDK1 interaction is shifted towards the associated form. The interaction of PKB PH domain with the lipids induces a change in conformation of PKB, noted as “PH-out”. In this conformation, Thr 308 becomes accessible to PDK1 (the phosphorylation sites are represented by yellow circles). After phosphorylation of Ser 473 and Thr 308 and loading of ATP, PKB dissociates from the plasma membrane in its active conformation to return to the cytoplasm and the nucleus. PKB re-adopts an inactive conformation upon dephosphorylation of its Thr 308 and Ser 473 sites