Figure 9. Role of the PEXEL in export of Plasmodium falciparum proteins to the infected erythrocyte.
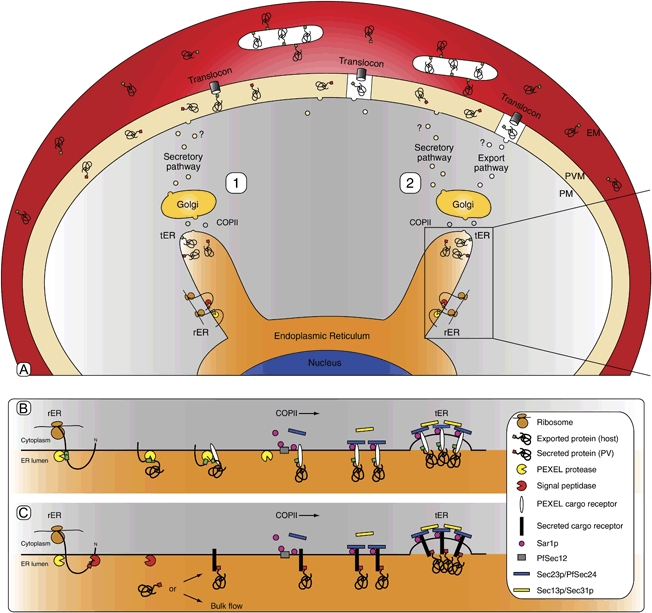
Two proposedmodels of PEXEL-mediated export are shown (A, 1 and 2). A1) After cotranslational insertion through Sec61 at the rough endoplasmic reticulum (rER) using the signal sequence, proteins to be exported are either processed by signal peptidase (red pac-man) or sequestered and/or processed by the PEXEL protease (yellow pac-man) and sorted at the transitional endoplasmic reticulum (tER) for transport through the Golgi to the parasitophorous vacuole by the default secretory pathway. There, proteins to be exported (xE/Q/D after PEXEL processing; green protein), are recognised and trafficked across the parasitophorous vacuole membrane by a translocon. Secreted or mutated PEXEL proteins are depicted as red proteins. A2) After entry at the rER and sequestration and/or processing by either signal peptidase (red pac-man) or the PEXEL protease (yellow pac-man), proteins to be exported are differentially sorted either at the tER or at the Golgi into vesicles. This may occur through a specific transmembrane PEXEL cargo receptor that enriches functionally distinct vesicles for exported proteins (green proteins), which are targeted to subcompartments (the ‘necklace of beads’; depicted as white compartments in the parasitophorous vacuole) of the parasitophorous vacuole that houses the translocon. Exported transmembrane proteins then presumably diffuse laterally from the translocon and traffic with forming Maurer's clefts (white structures in the erythrocyte). Secreted proteins (red) traffic through the default secretory pathway to alternative compartments of the parasitophorous vacuole that do not contain the translocon. The default pathway may involve bulk flow, depicted as free red proteins in the ER that ‘sample’ the budding membrane. Uncharacterised vesicles are depicted by ‘?’. Close up (box) of the possible sorting mechanism is shown in (B) and (C). B) After cotranslational insertion into the rER PEXEL proteins are sequestered/processed by the PEXEL protease and sorted into vesicles through a transmembrane cargo receptor that interacts with the COPII machinery. C) Secreted proteins are not recognised by the PEXEL receptor but bind either a different receptor or traffic through bulk flow. The role of the Golgi is unclear but similar sorting may occur there.
