Fig. 7.
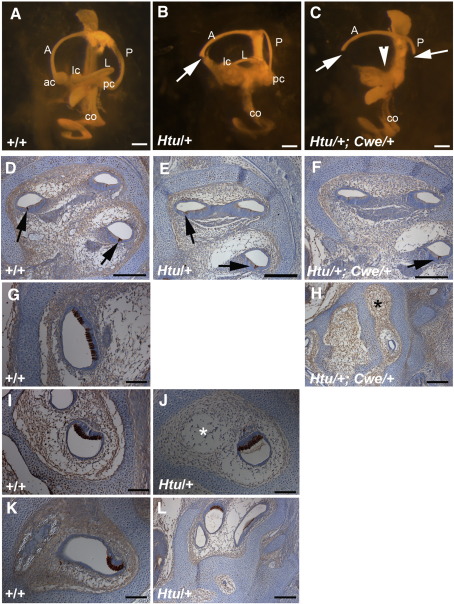
Mice double heterozygous for the catweasel and headturner mutation have truncations of all three semicircular canals and lack the cristae. (A–C) Analysis of gross morphology of the inner ear of wildtype, Htu/+ and Htu/+;Cwe/+ mice at E16.5 by paintfilling. (A) Wildtype embryos have a fully developed inner ear with clearly distinguishable semicircular canals and cristae. (B) Htu/+ embryos always have anterior canal truncations (white arrow) and sometimes posterior canal truncations (not shown). (C) Htu/+;Cwe/+ embryos always have anterior and posterior canal truncations, and in addition have lateral canal defects (arrowhead pointing to area where the lateral semicircular canal is missing). No cristae ampulare can be identified (D–L) Sections through the inner ear stained for Myo7a protein expression of wildtype, Htu/+ and Htu/+;Cwe/+ embryos at E16.5. (D–F) Sections through the cochlea of a wildtype, Htu/+ and Htu/+;Cwe/+ embryos shows normal gross morphology. (G) A section through a wildtype anterior crista expressing Myo7a. (H) A section through the vestibular system of a Htu/+;Cwe/+ embryo. No Myo7a-positive cristae could be identified. Note the absence of the anterior canal (⁎). (I) A Myo7a-positive lateral crista in a wildtype embryo. Note on the top left the anterior canal is visible (J) Htu/+ embryos have normal lateral cristae. Note the absence of the anterior canal (⁎). (K) A section through an wildtype posterior crista expressing Myo7a. (L) This Htu/+ embryo lacks the posterior crista. Scale bars: A–C = 1 mm, D–L = 200 μm. A, anterior semicircular canal; ac, anterior crista; co, cochlea; L, lateral semicircular canal; lc, lateral crista; P, posterior semicircular canal; pc, posterior cristae.