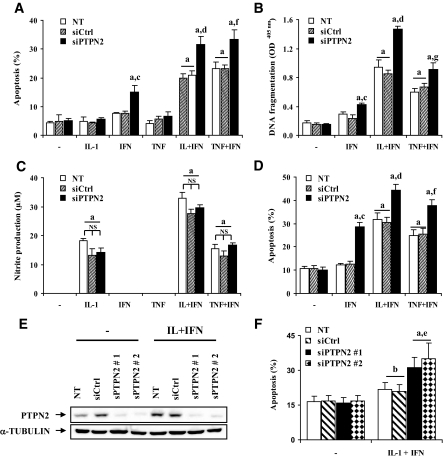
FIG. 4.
siRNA-mediated PTPN2 inhibition exacerbates cytokine-induced apoptosis in INS-1E cells, primary rat β-cells, and dispersed human islets, independently of NO production. INS-1E cells were transfected and treated as described in Fig. 3. Apoptosis was evaluated after 24 h using HO/PI staining (A) and a Cell Death Detection ELISAplus kit (B). C: INS-1E cells were transfected and treated as described in Fig. 3, and nitrite concentrations in supernatants were measured as described in research design and methods (D). Primary fluorescence-activated cell–sorted rat β-cells were cultured for 2 days and then transfected as described in Fig. 3. After 2 days of recovery, cells were left untreated (NT) or treated for 72 h with IFN-γ (100 units/ml), IL-1β (10 units/ml) + IFN-γ (100 units/ml), or TNF-α (1,000 units/ml) + IFN-γ (100 units/ml). E and F: Dispersed human islets were left untransfected, or transfected with 30 nmol/l of siCtrl or human siPTPN2 #1 or #2 and cultured for a 48-h recovery period. Cells were then treated with IL-1β (50 units/ml) + IFN-γ (1,000 units/ml) for 48 h when PTPN2 and α-tubulin were evaluated by Western blot (E) and 96 h when apoptosis was evaluated by HO/PI staining (F). Results are means ± SE of four experiments; a: P < 0.001 and b: P < 0.05 vs. untreated NT or untreated transfected with the same siRNA; c: P < 0.001 vs. IFN-γ–treated NT and siCtrl, d: P < 0.001 and e: P < 0.05 vs. IL-1β + INF-γ–treated NT and siCtrl, f: P < 0.001 and g: P < 0.05 vs. TNF-α + INF-γ–treated NT and siCtrl; ANOVA followed by Student's t test with Bonferroni correction.