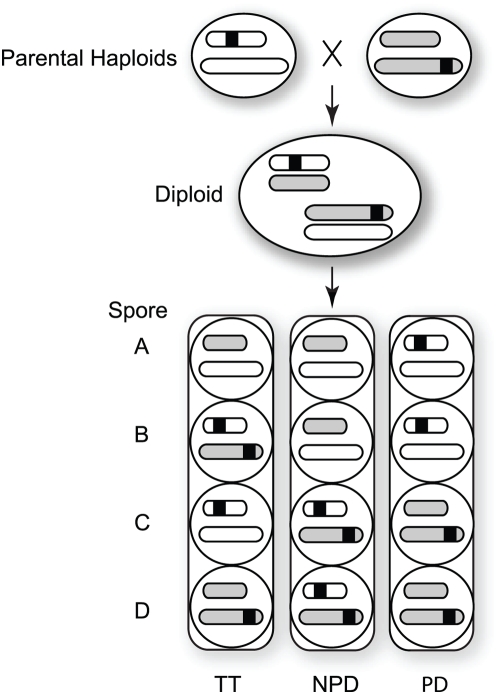
Figure 1. Segregation in a cross between strains carrying a transposed segment.
In this example, two haploid parental strains harbor a particular genomic region (black) on different chromosomes. Crossing the parents leads to a diploid that contains two copies of the transposed segment. Sporulation leads to either a tetratype (TT) pattern (one duplication and one deletion); a non-parental ditype (NPD) pattern (two duplications and two deletions), or a parental ditype (PD) pattern (neither duplications nor deletions). The relative frequencies depend on the position of the transposed segment relative to the centromeres in each parent.