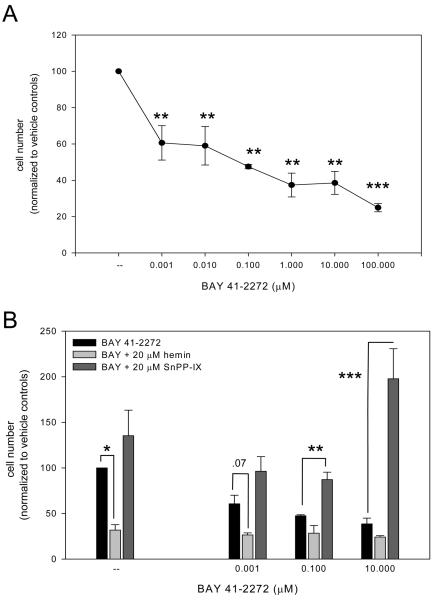
Figure 1.
A: Incubation of rat A7R5 VSM cells with BAY 41-2272 (0.001-100 μM) in 10% FBS significantly (p < .001) reduces cell growth in dose-dependent fashion after 72 hours as measured with fluorescent nucleic acid staining. Comparable growth-inhibitory effects of BAY were observed using hemacytometry and automated cell counting (data not shown). Results are mean ± SEM, and n = 3 experiments/group. *Statistically significant with p < .05, ***statistically significant with p < .001 versus normalized DMSO vehicle controls. B: Concomitant treatment of cells with BAY and the HO inducer hemin (20 μM) significantly reduced cell numbers (p = .026) at each BAY concentration while HO inhibition by tin protoporphyrin-IX (SnPP-IX; 20 μM) significantly increased cell numbers (p = .022) compared to exclusive BAY treatments. Post-hoc results: *statistically significant with p < .05, **statistically significant with p < .01, ***statistically significant with p < .001 versus BAY 41-2272 treatment only. Trypan blue exclusion staining did not reveal significant reduction in cell viability in any treatment group (data not shown). Results are mean ± SEM, and n = 3 experiments/group.