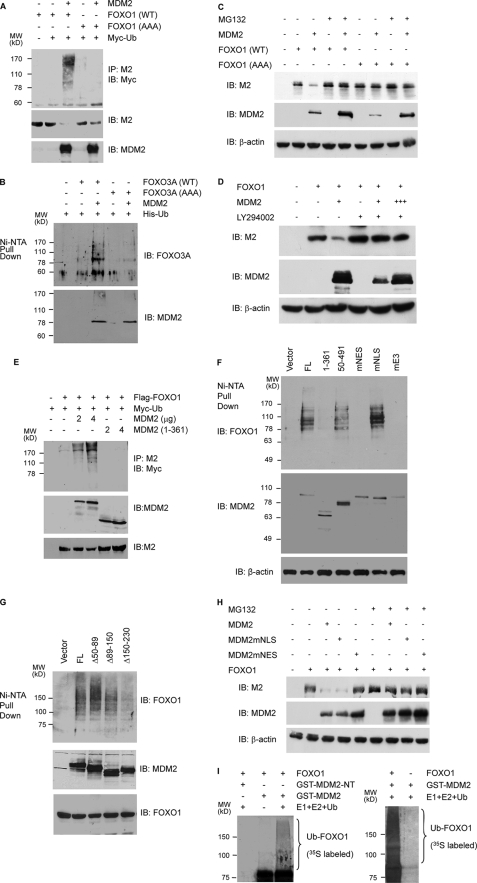
FIGURE 5.
MDM2 promotes the ubiquitination and degradation of FOXOs in a manner dependent on AKT-mediated phosphorylations and cytoplasmic localization. A, MDM2 promotes the ubiquitination of FOXO1 in vivo. H1299 cells were transfected with the indicated vectors. Cellular extracts were prepared, and FOXO1 ubiquitination was determined by precipitations (IP) with M2 anti-FLAG followed by immunoblotting (IB) with a Myc antibody (upper panel). The level of FOXO1 and MDM2 expression (lower panels) was determined by immunoblotting of the cellular extracts. B, MDM2 promotes the ubiquitination of FOXO3A in vivo. H1299 cells were transfected as indicated. Cellular extracts were subjected to Ni2+-NTA bead pull-down assays followed by immunoblotting with an HA antibody (upper panel). The level of MDM2 expression was determined by immunoblotting of the cellular extracts (lower panel). C, MDM2 promotes the FOXO1 degradation. H1299 cells were transfected with 2 μg of the indicated plasmids. 24 h later, the cells were treated with either DMSO (–) or 10 μm MG132 for 6 h. Cellular extracts were subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. D, effect of LY294002 on the ability of MDM2 to decrease FOXO1 expression. PC3 cells were transfected with 2 μg of FLAG-FOXO1 and 2 (+) and 6 (+++) μg of MDM2. 15 h later, the cells were treated with either DMSO or 10 μm LY294002 for 8 h. Cellular extracts were subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. E, dose-dependent effect of MDM2 on FOXO1 ubiquitination and the requirement of its carboxyl-terminal RING domain. p53 and MDM2 double null MEFs were transfected with the indicated vectors, and the ubiquitination of FOXO1 and the level of FOXO1 and MDM2 expression were determined by immunoblotting of the cellular extracts. F and G, ubiquitination of FOXO1 requires MDM2 E3 ligase activity, cytoplasmic localization, and interaction with FOXO1. p53 and MDM2 double null MEFs were transfected with the indicated vectors, and the ubiquitination of FOXO1 as well as the level of FOXO1 and MDM2 expression were determined by immunoblotting of the cellular extracts. H, the dependence on cytoplasmic localization for the ability of MDM2 to decrease FOXO1 level. H1299 cells were transfected with 2 μg of FLAG-FOXO1 and MDM2. 24 h later, the cells were treated with either DMSO or 10 μm MG132 for 6 h. I, MDM2 promotes FOXO1 polyubiquitination in vitro. GST-MDM2 and GST-MDM2-(1–150) (GST-NT) were produced in E. coli and bound to glutathione-agarose beads, and the ubiquitination of the bound FOXO1 protein was assayed as described under “Materials and Methods.” Ubiquitinated FOXO1 was visualized by autoradiography as a high molecular weight smear above the unmodified FOXO1 band.