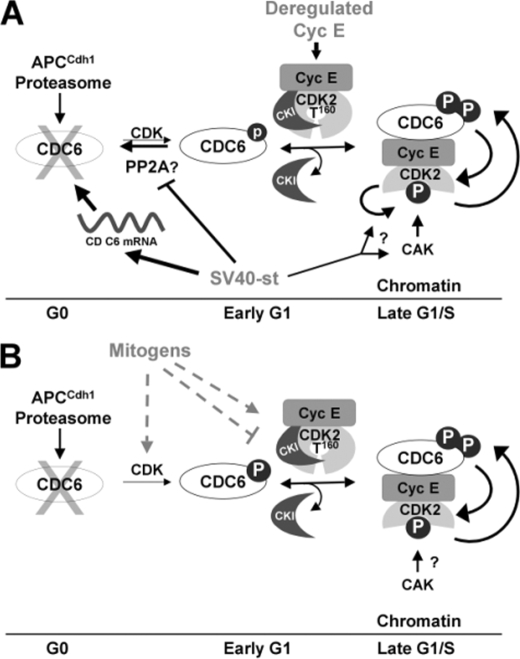
FIGURE 8.
Model of events linking CDC6 and CDK2 activation during exit from quiescence induced by cyclin E and st coexpression or mitogens. A, expression of st and deregulated cyclin E expression in quiescent NHF result in cooperative activation of the essential origin licensing factor CDC6 and coordinated CDK2 activation. st potently induces CDC6 mRNA expression and to a lower extent CDC6 phosphorylation on a CDK site(s) and stabilization. st also facilitates loading of CKI free cyclin E/CDK2 onto chromatin, which correlates with CDK2 phosphorylation on the activating T loop. CDC6 may facilitate CAK access to the CDK2 T loop, which could be prevented by CKIs. Alternatively st may induce CDK2 autophosphorylation on Thr-160 (arrow with question mark; see text). Coexpression of cyclin E and st also enhances CDC6 phosphorylation and loading onto chromatin suggesting positive feedback loops leading to activation of CDK2 and CDC6 accumulation (indicated by reciprocal arrows). B, mitogens may use similar mechanisms to activate CDK2 on chromatin.