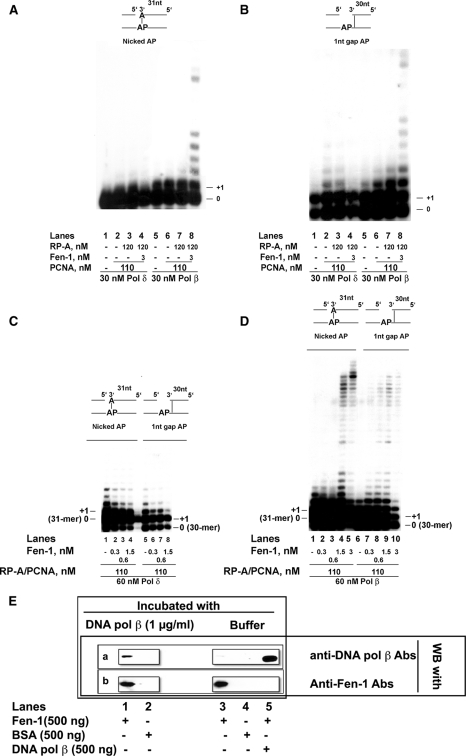
FIGURE 5.
Fen-1 influences both the incorporation and elongation steps by DNA polymerases δ and β during abasic site bypass and can physically interact with DNA polymerase β. The reactions were performed as described under “Experimental Procedures.” A, 30 nm DNA pol δ (lanes 1–4) or DNA pol β (lanes 5–8) were incubated on the nicked AP template in the absence (lanes 1 and 5) or in the presence of PCNA either alone (lanes 2 and 6) or in combination with RP-A (lanes 3 and 7) or 120 nm RP-A together with 3 nm Fen-1 (lanes 4–8). B, as in A but on the 1-nt gap AP template. C, 60 nm DNA pol δ were incubated on the nicked AP (lanes 1–4) or on the 1-nt Gap AP (lanes 5–8) templates, in the presence of a combination of equimolar amounts of PCNA and RP-A (110 nm), and in the absence (lanes 1 and 5) or in the presence (lanes 2–4 and 6–8) of increasing amounts of Fen-1. D, as in C but in the presence of 60 nm DNA pol β. E, 500 ng of Fen-1 (lanes 1, 3, and 5), BSA (lanes 2 and 4) or DNA pol β (lane 5) were incubated either in the presence (lanes 1 and 2) or in the absence (lanes 3–5) of DNA pol β. The membranes were developed either with anti-Fen-1 (membrane a) or anti-DNA pol β (membrane b) antibodies, and the signals were detected by chemiluminescence.