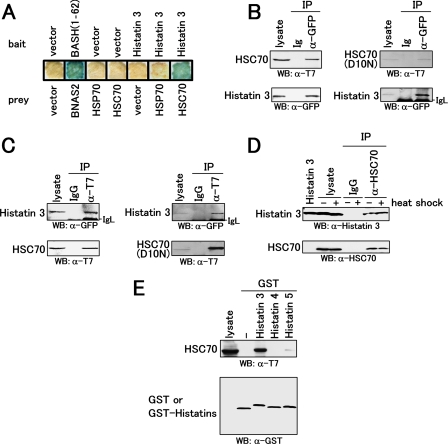
FIGURE 1.
Interaction of histatin 3 with heat shock protein HSC70. A, expression vectors encoding histatin 3 (bait) and heat shock proteins (prey) were transformed into yeast L40. Transformants were cultured on a membrane filter, and a β-galactosidase assay was performed. Vector and BASH-(1–62)/BNAS2 represent empty and positive control vectors, respectively. B, COS-7 cells were co-transfected with expression vectors encoding CFP-tagged histatin 3 and T7-tagged HSC70 or T7-tagged HSC70(D10N). Proteins extracted from COS-7 cells were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-GFP serum and control serum (Ig). Precipitates as well as cell lysates (lysate) were analyzed by Western blotting (WB) with anti-T7 antibody (top) and anti-GFP serum (bottom). C, proteins extracted from COS-7 cells were immunoprecipitated with anti-T7 antibody and control IgG. Precipitates were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-GFP serum (top) and anti-T7 antibody (bottom). D, HGFs were cultured with histatin 3 under non-heat (-) and heat (+) shock conditions. Proteins extracted from cells were immunoprecipitated with anti-HSC70 antibody. Precipitates were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-histatin 3 (top) and anti-HSC70 (bottom) antibodies. E, GST pulldown assays for members of the histatin family and HSC70. An expression vector encoding T7-tagged HSC70 was transfected into COS-7 cells. Proteins extracted from COS-7 cells were mixed with GST and GST-fused histatins 3, 4, and 5 that had been immobilized to glutathione-Sepharose beads. Precipitates were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-T7 (top) and anti-GST (bottom) antibodies.