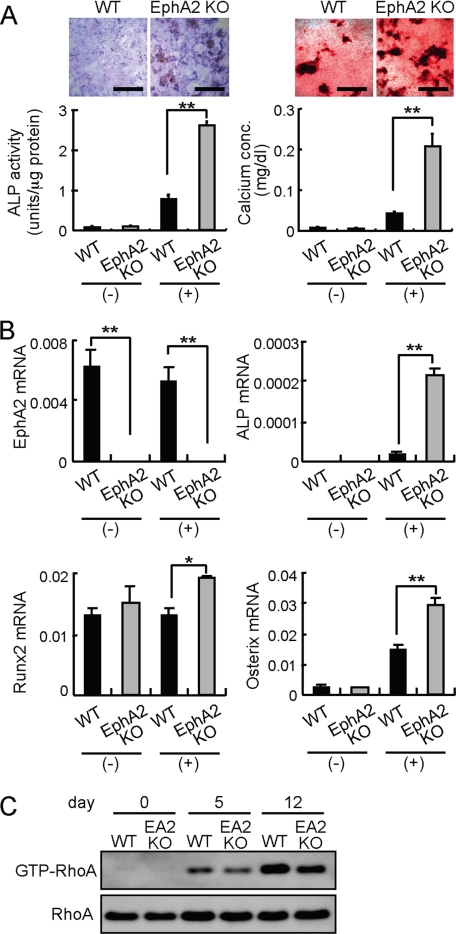
FIGURE 5.
EphA2 signaling inhibits osteoblast differentiation. A, differentiation of wild-type (WT) and EphA2-deficient (EphA2 KO) calvarial osteoblasts. Osteoblast precursors were cultured in the absence (-) or presence (+) of ascorbic acid and β-glycerophosphate. ALP staining (upper left panels) and calcium staining (upper right panels) were performed after 6 and 13 days, respectively. Scale bars, 500 μm. ALP activities and calcium concentrations were quantified. B, qRT-PCR analysis of osteoblast markers in WT and EphA2 KO calvarial osteoblasts cultured under non-osteoblastogenic (-) or osteoblastogenic (+) conditions. RNAs were prepared on day 8. Error bars represent means ± S.E. (n = 3). *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01 versus controls shown in black bars. C, RhoA activities in differentiating osteoblasts lacking EphA2. day, after addition of ascorbic acid and β-glycerophosphate.