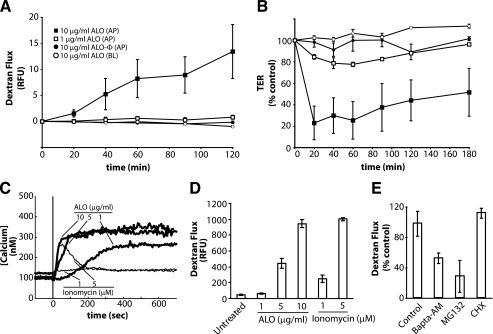
FIGURE 1.
ALO induces C2BBE monolayer permeability. A, 3-kDa dextran-fluorescein flux in C2BBE monolayers treated apically (AP) or basolaterally (BL) with ALO or heat-inactivated ALO (ALO-Φ) at 1 μg/ml or 10 μg/ml. Flux is quantified by basolateral relative fluorescence units (RFU). B, transepithelial resistance of C2BBE monolayers treated with ALO at 1 or 10 μg/ml. Symbols represent the same conditions as seen in A. C, intracellular Ca2+ levels in C2BBE monolayers during ALO (thick lines) or ionomycin (thin lines) treatment. The monolayers were perfused with HBSS (which contains 1.26 mm Ca2+) and treated with either ALO or ionomycin at the indicated concentrations at time = 0 s (vertical line). D, dextran-fluorescein flux across C2BBE monolayers treated apically with ALO (0, 5, or 10 μg/ml) or ionomycin (1 or 5 μm) for 2 h. E, ALO (1 μg/ml) induced dextran-fluorescein flux across the C2BBE monolayer after pretreatment of C2BBE monolayers with either the proteasome inhibitor, MG132 (10 μm), for 2 h or BAPTA-AM (10 μm) for a 30-min pretreatment and 2-h treatment. Error bars, S.E. CHX, cycloheximide.