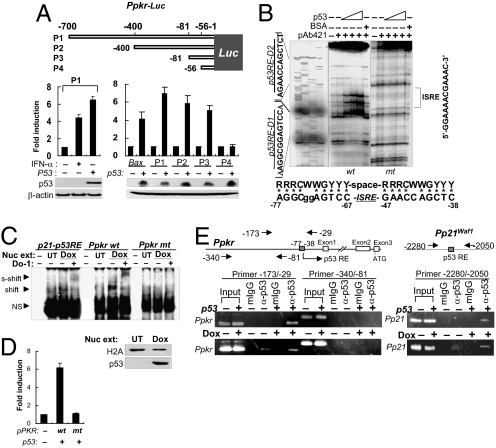
Fig. 2.
p53 acts directly on the PKR promoter. (A) Promoter deletion assay using luciferase reporters (Ppkr-Luc). Luciferase activities were assessed in p53-transfected HCT116 (p53−/−) cells. Results are reported as mean ± SEM (n = 3). (B) DNase I footprinting with 32P-labeled wild-type (wt) and mutant (mt, sequence shown in Fig. S4) PKR promoter fragments (-160/-29) and p53 protein (BaculoV-p53). Consensus p53RE sequence is aligned with the identified Ppkr-p53RE sequence (Lower). (C) EMSA using nuclear extracts (Nuc ext) obtained from doxorubicin-treated HCT116 p53+/+ cells (Dox), 32P-labeled PKR81/-29/p21 promoter fragments, and α-p53 antibody (DO-1). Nuclear extracts were assessed with anti-histone 2A (H2A) antibody and DO-1 (Lower). UT, untreated; NS, nonspecific. (D) Luciferase reporter assay with wild-type (wt) and mutant (mt) PKR promoters (Ppkr) used in EMSA in panel C and in Fig. S4B. Luciferase assay was performed 48 h after transfection of HCT116 p53+/+ cells with wild-type or mutant PKR promoter (Ppkr-81/-29)-attached luciferase reporters together with p53-expressing plasmid (1 μg pCDNA-p53). Data shown are from 3 independent experiments and are expressed as means ± SEM. (E) ChIP assay with chromatins obtained from p53-transfected HCT116 (p53−/−) cells or from doxorubicin-treated (0.5 μM for 12 h) p53+/+ cells (Dox), and DO-1 (α-p53) or control mouse IgG (mIgG).