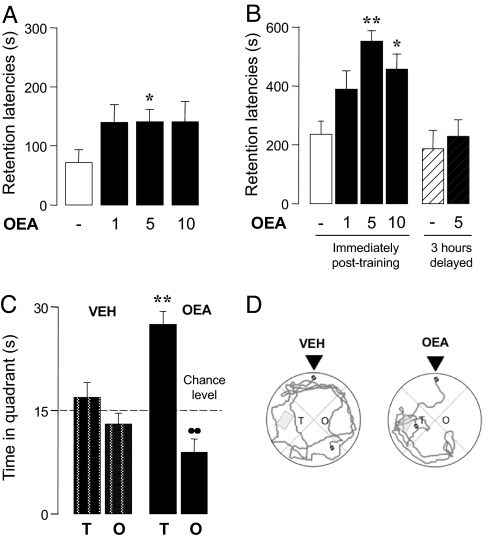
Fig. 1.
OEA enhances memory consolidation in the inhibitory avoidance (A, B) and water maze (C, D) tasks. (A, B) Performance in the 24-hour retention test (mean ± SEM) of (A) Wistar rats given pretraining injections of OEA (mg·kg−1, i.p., H3 = 7.871, P = 0.049, n = 12), and (B) Sprague-Dawley rats given post-training injections of OEA either immediately (open and filled bars, H3 = 15.023, P = 0.0009, n = 11–15) or 3 hours after training (striped bars). Post hoc comparisons: *, P < 0.05 and **, P < 0.01 vs. vehicle. (C) Time (mean ± SEM) spent during the 1-minute probe trial (48 hours after training) in target (T) and opposite (O) quadrants by rats injected with vehicle (open bars) or OEA (5 mg·kg−1, i.p., filled bars) immediately after training. Two-way ANOVA showed a significant treatment × quadrant interaction (F1,44 = 15.146, P = 0.0003, n = 11–13). **, P < 0.01 within quadrants; ●●, P < 0.01 within treatment. (D) Representative swimming paths of animals treated with vehicle or OEA (5 mg·kg−1, i.p.) immediately after training. Arrows indicate starting positions.