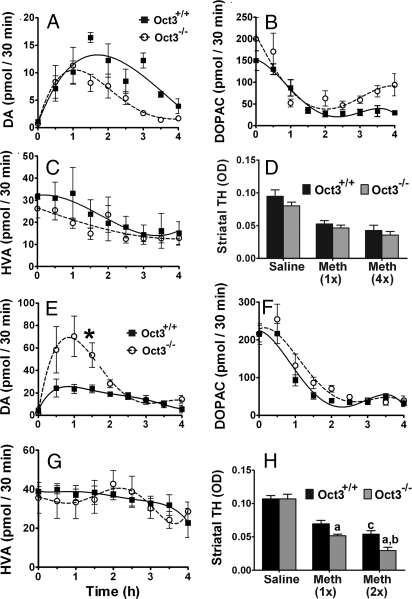
Fig. 5.
Oct3 ablation increased extracellular levels of DA and striatal neurotoxicity in methamphetamine injected mice. Striatal microdialysis dialysates were collected every 30 min for 1 h before methamphetamine injections (A–C: 5 mg/kg i.p., E–G: 30 mg/kg s.c.) for baseline measurements (pooled for 0 time point) and for an additional 4 h after the injection, followed by HPLC analyses for DA (A and E) and its metabolite levels (B, C, F, and G). Data represent mean ± SEM, n = 4–5 per genotype. Areas under the curve were generated using GraphPad Prism followed by a 2-tailed t test. *, P < 0.05 compared to the Oct3+/+ group. In other separate studies, animals were injected with either 5 mg/kg i.p. (single or every 2 h for 4 injections, D) or 30 mg/kg s.c. (single or 2 injections 4 h apart, H) and processed for striatal dopaminergic terminal density (D and H). Data represent mean ± SEM, n = 3–5 per group (D), n = 6–9 per group (H), (a) P < 0.05 compared to the respective Oct3+/+ methamphetamine group, (b) P < 0.01 compared to the Oct3−/− methamphetamine 1 injection group, (c) P < 0.05 compared to the Oct3+/+ methamphetamine 1 injection group, analyzed by 2-way ANOVA with treatments crossed with genotypes (genotype: F1,38 = 11.19, P = 0.002; treatment: F2,38 = 78.86, P < 0.001) followed by the Newman-Keuls post hoc test.