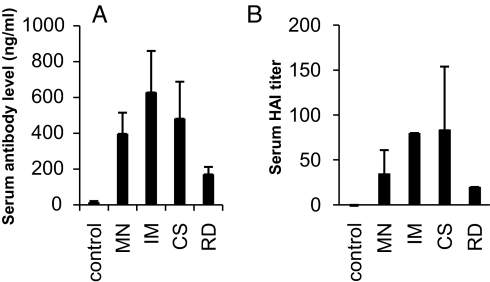
Fig. 3.
Comparison of antibody responses induced in mice after immunization by coated MNs or IM injection of IIV vaccines. Five groups of mice (6 per group) were used in the immunization study. Group 1 mice (control) received immunization by MNs coated with 10 μg of BSA. Group 2 mice (MN) received immunization by MNs coated with 10 μg of IIV (3 arrays were used per mouse, each coated with 3.3 μg of virus). Group 3 mice (IM) received IM injection of 10 μg of IIV dissolved in PBS. Group 4 mice (CS) received IM injection of 10 μg of IIV dissolved in MN-coating solution. Group 5 mice (RD) received 10 μg of virus that was redissolved from coated MNs in PBS. Sera were collected on day 14 after immunization and analyzed for antibody responses against influenza virus. (A) Antibody responses against the influenza HA protein. The levels of antibody responses against HA were determined by ELISA using purified HA proteins as coating antigens and are expressed as the amount of HA-specific antibodies in 1 mL of serum samples (ng/mL). (B) HAI activity of sera from immunized mice. The HAI activity was determined as described in Materials and Methods and is expressed as the highest dilution that resulted in complete inhibition of hemagglutination (HAI titer). Data are presented as the mean ± SD.