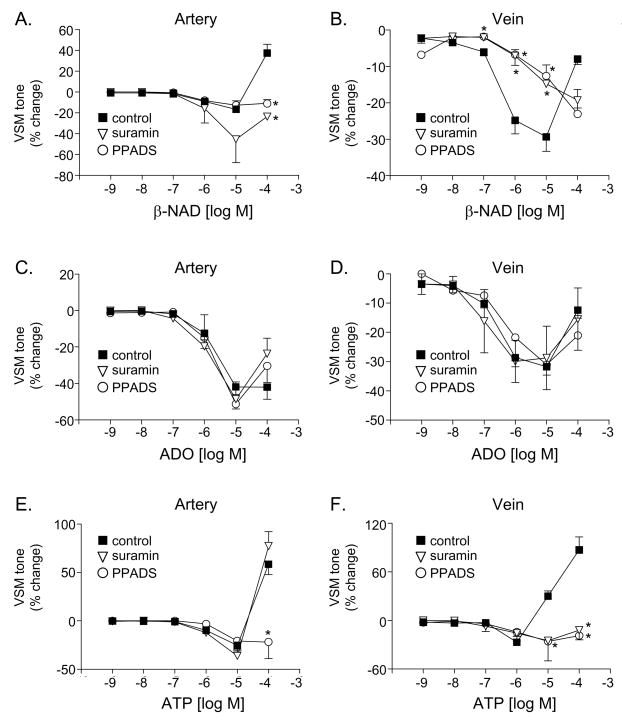
Fig. 7.
The effects of β-NAD (A, B), adenosine (ADO, C, D) and ATP (E, F) in the absence (closed squares) and presence of the P2 receptor antagonists suramin (100 μM) or PPADS (30 μM) in the canine mesenteric artery (left column) and vein (right column). Data represent mean±SEM from 2–6 experiments. The asterisks denote significant difference from controls in the absence of P2 receptor antagonists, P<0.05.