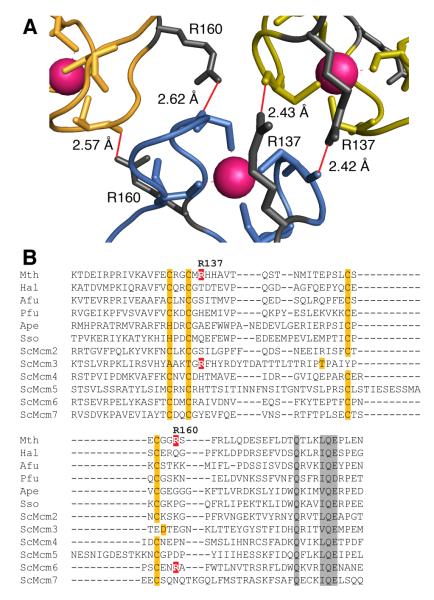
Fig. 1. Identification of R137 and R160 as residues potentially involved in ring-ring interactions.
(A) Detail of the hexamer-hexamer interface from the crystal structure of the N-terminal domain of MthMCM ((15); Pdb reference: 1LTL) The α-carbon traces for two monomers from the top hexamer (green and yellow) and one from the bottom hexamer (blue) are shown; Zinc atoms are in magenta. The hydrogen bonding pattern involving R137 and R160 with main chain carbonyls is shown in red. The figure was generated with MacPyMol (DeLano Scientific, USA).
(B) ClustalX (40) alignment of zinc-finger regions of various MCM proteins. Zinc-finger residues are highlighted in orange, other conserved residues are highlighted in grey. R137 and R160, and corresponding arginines in other MCMs are indicated in white on red. Species names are abbreviated as follows: Mth, Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus; Hal, Halobacterium sp. pNRC-1; Afu, Archaeoglobus fulgidus; Pfu, Pyrococcus furiosus; Ape, Aeropyrum pernix; Sso, Sulfolobus solfataricus; Sc, Saccharomyces cerevisiae.