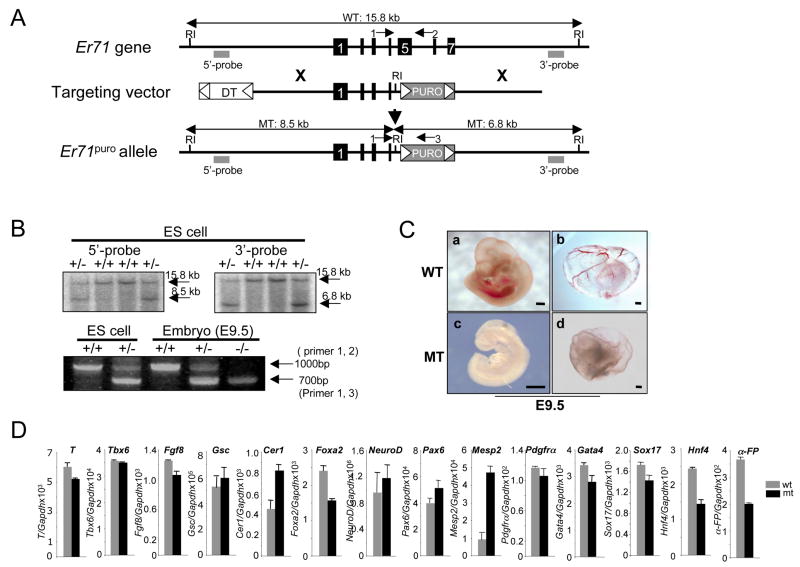
Figure 5. Disruption of the murine Er71 locus.
(A) Structures of the mouse Er71 gene, the pGKpuro targeting vector, and the targeted allele after homologous recombination. Black boxes depict exons. The flanking genomic probes used for Southern blot analysis are indicated with gray squares. Only the EcoRI restriction enzyme site relevant to the targeting construct and screening strategies is shown. (B) Southern blot analyses of representative Er71+/− ES cell clones and genotyping of ES cells and E9.5 embryos by PCR. The wild type (15.8kb) and the mutant allele (8.5kb) detected with the 5′ external probe as well as the wild type (15.8kb) and the mutant allele (6.8kb) detected with the 3′ external probe after EcoRI digest are shown. PCR products of the wild type Er71 allele (primer 1, 2: 1000 bp) and the mutant allele (primer 1, 3: 700 bp) are shown. (C) Gross morphology of Er71−/− embryos at E9.5. (a, c, embryo proper; b, d, yolk sac). Scale bars; 200 μm. (D) Gene expression analysis. RNA was prepared from E8.5 (n=2) embryos and subjected to qRT-PCR. The value normalized against Gapdh is shown on the Y-axis.