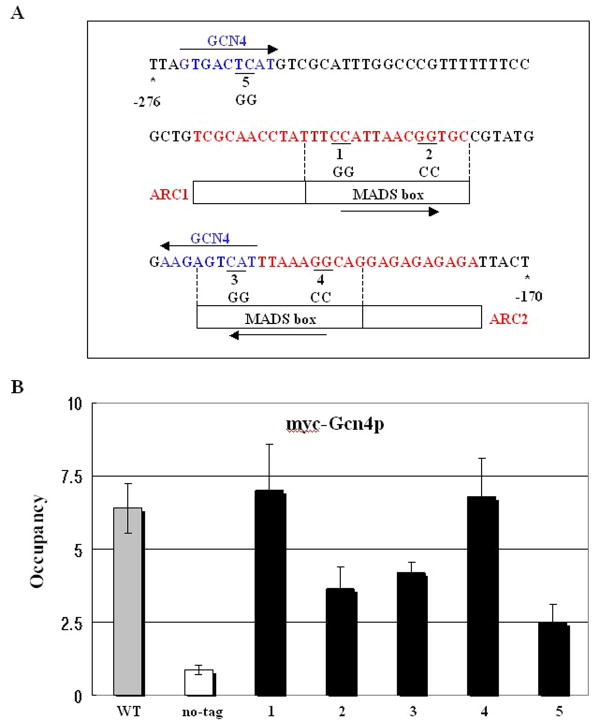
Figure 1. Gcn4p binding is reduced by point mutations in the MADS box.
(A) Nucleotide sequence of the ARG1 promoter region. The sequence is numbered (-276 to -170, indicated by asterisks) relative to the main transcription start site. The Gcn4p binding sites (GTGACTCAT and AAGAGTCAT) are overlined and designated with blue. The site-directed mutagenized sequences are underlined with black and indicated below by numbers (1 to 5). There are two arginine control elements (ARC1 and ARC2), which are binding sites for the ArgR/Mcm1p repressor complex, indicated by red letters and boxes. The putative Mcm1p binding sites are boxed within the ARC elements and designated as MCM1, AGAMOUS, DEFICIENS, and serum response factor (MADS) boxes. The two Gcn4p binding sites and MADS boxes are in opposite orientations and designated with arrows. (B) The gcn4Δ SS5 strains containing mutations in the ARG1 alleles are indicated below the histogram; WT (SY722), mutant 1 (SY772), mutant 2 (SY723), mutant 3 (SY583), mutant 4 (SY724), and mutant 5 (SY773). The strains were transformed with a single-copy GCN4-myc plasmid (pSK1). For the non-tagging (no-tag) condition, gcn4Δ (SY722) strains were transformed with an empty vector. ChIP analysis of the transformants was conducted to measure binding of myc-Gcn4p to ARG1, as described in Materials and Methods and Supporting Information. The percentage of ARG1 UAS that immunoprecipitated with myc antibodies was measured for each strain and normalized to the nonspecific immunoprecipitation of POL1 ORF sequences (Occupancy).