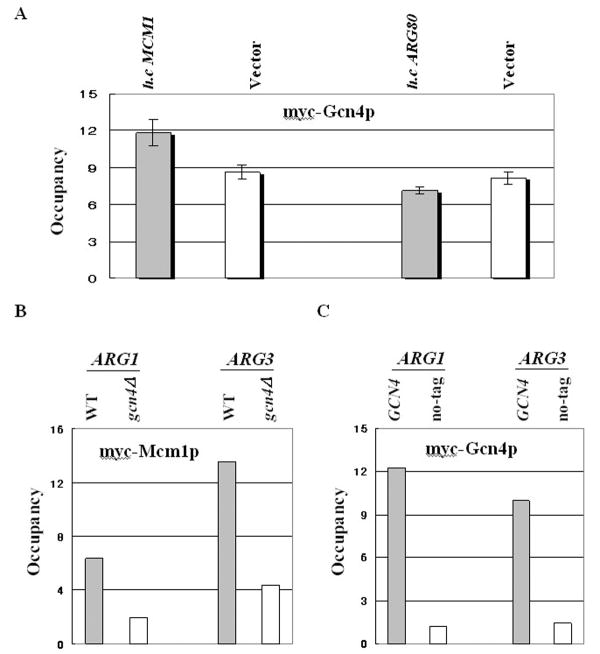
Figure 2. Mcm1p binding levels positively correlate with Gcn4p binding levels at Gcn4p target promoters.
(A) The transformants of gcn4Δ (249) strains containing myc-tagged GCN4 plasmid (pSK1) were re-transformed with an empty vector, a high-copy plasmid pED40 harboring MCM1, or high-copy plasmid pSY365 harboring ARG80. ChIP analysis of the transformants was conducted to measure binding of myc-Gcn4p to ARG1 UAS, as described in Fig. 1B. (B) The target genes (ARG1 and ARG3) of Gcn4p are indicated above the histogram. High-copy plasmid pHQ1239 harboring the GCN4-HA allele was introduced into WT MCM1-myc (SY337) strains. An empty vector was introduced into the gcn4Δ MCM1-myc (SY339) strains. ChIP analysis of the transformants was conducted to measure binding of myc-Mcm1p to ARG1 UAS or to ARG3. Signals for ARG1 UAS or ARG3 in the immunoprecipitate (IP) were normalized to the corresponding POL1 signal and plotted in the histogram (Occupancy). (C) The gcn4Δ (249) strains were transformed with an empty vector (no-tag) or myc-tagged GCN4 plasmid (pSK1). ChIP analysis of the transformants was conducted to measure binding of myc-Gcn4p to ARG1 UAS or ARG3, as described in Fig. 2B.