Fig. 7. Schematic model of Ser5P-stimulated BUR1/BUR2 recruitment and differential contributions of BUR1/BUR2 and CTK1 to Ser2P and H3-K36Me3 formation at 5′ and 3′ ends of a coding sequence.
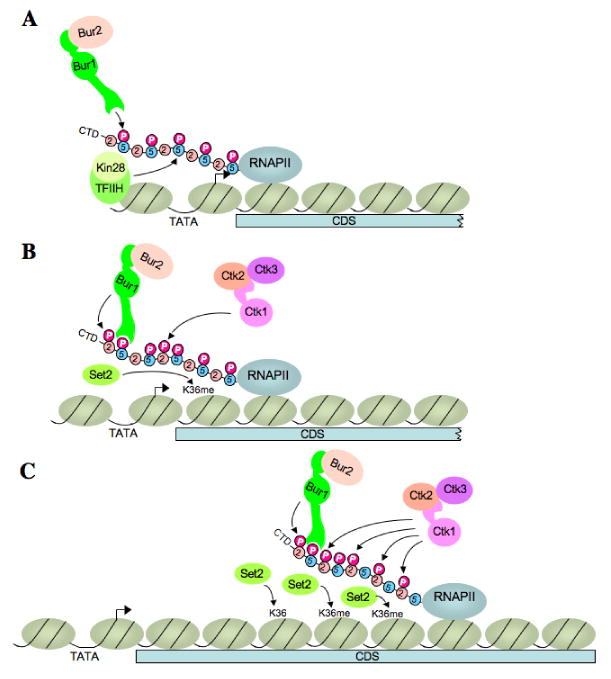
(A) BUR1/BUR2 is recruited to the CTD phosphorylated on Ser5 by KIN28 at or near the promoter. (B) Recruited BUR1/BUR2 phosphorylates Ser2 near the promoter, enhancing H3-K36Me3 formation by SET2. It is unknown whether Pol II pausing early in the coding sequence (CDS) is required to facilitate BUR1/BUR2 function. BUR1/BUR2 and CTK1 make roughly equivalent contributions to Ser2P formation at this location. (C) As elongation proceeds downstream, CTK1 makes an increasingly larger contribution to Ser2P formation and attendant H3-K36Me3 formation by SET2. Because the occupancies of both kinases remain high at the 3′ end, either CTK1 becomes more active, or BUR1/BUR2 activity declines, as elongation proceeds. See text for more details.
