Figure 6.
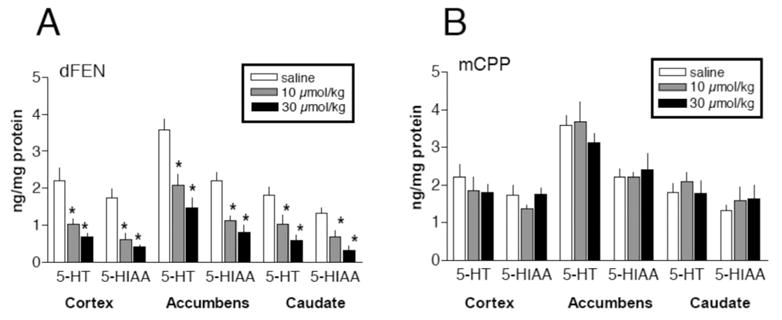
Effects of high-dose administration of d-fenfluramine (dFEN) or m-chlorophenylpiperazine (mCPP) on postmortem tissue levels of serotonin (5-HT) and its metabolite 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA) in rat brain. dFEN or mCPP was administered ip at doses of 10 or 30 μmol/kg, every 2 h, for four doses. Rats were killed two weeks after the dosing regimen. Postmortem tissue levels of 5-HT and 5-HIAA in prefrontal cortex, nucleus accumbens, and caudate nucleus were determined by high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection (HPLC-ECD). These doses of dFEN and mCPP produce equivalent increases in extracellular 5-HT. Data are mean ± SEM, expressed as ng/mg protein for N = 4–6 rats/group. * p < .05 compared with saline-treated group (Duncan’s post hoc test). Data taken from Baumann et al. (2001).
