Figure 2. Vascular expression of Rasip1 in embryonic organs and tissues.
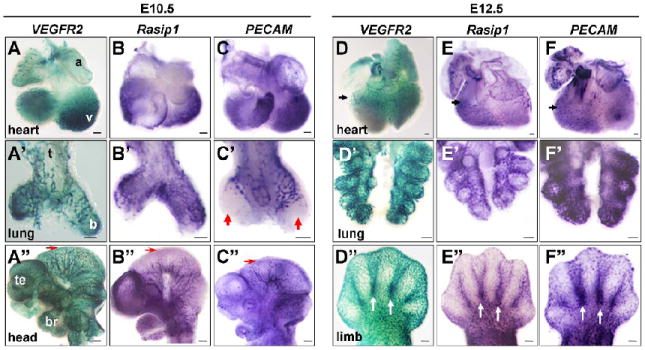
Flk1(VEGFR2)-lacZ whole mount β-galactosidase staining and whole mount in situ hybridization of vascular markers in isolated embryonic tissues, at stages indicated. A,D columns) Whole mount β-galactosidase staining using Flk1(VEGFR2)-lacZ embryos. Whole mount in situ hybridization of Rasip1 (B,E columns) and PECAM (C,F columns). A-F) Hearts. A’-F’) Lungs. A”-C”) Heads. D”-F”) Limb buds. Note similarity of expression of Rasip1 in most vessels, as marked by VEGFR2 and PECAM expression (black arrowheads). Expression of all three vascular markers can be observed in the endocardium of the ventricle trabeculae in the heart (A-C) and of the coronary vasculature (arrows, D-F). Expression of all three markers is evident in the proximal ECs of the early lung buds (A’-C’), although PECAM is not expressed in the ECs of the most distal tips of the buds at E10.5 (red arrowheads), while both VEGFR2 and Rasip1 are observed in this population. This heterogeneity is also observed in the cephalic vessels at E10.5, where VEGFR2 is robustly expressed in the most mediolateral/distal vessels of the mesencephalon, while Rasip1 and PECAM are expressed at lower levels (red arrows, A”-C”). Rasip1 is expressed in the vessels of the developing limb buds, including the interdigit vessels (white arrows, D”-F”). a, atria; b, bronchus; br, branchial arches; t, trachea; te, telencephalon; v, ventricle. The scale bars represent 100μm in A-F’ and 250μm in A”-F”.
