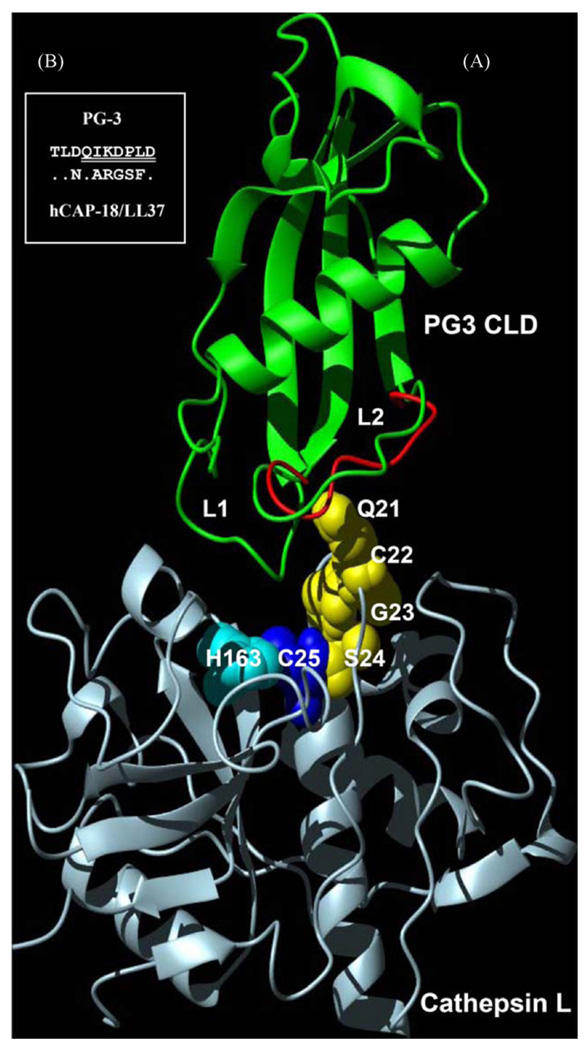
Fig. 4.
Hypothesized complex model between PG3 CLD and cathepsin L. (A) The L2 loop of PG3 CLD with conformational flexibility due to the prolyl cis–trans isomerization is close to the active site of cathepsin L in which a putative conformational pathway mediated by Q21-S24 of cathepsin L (highlighted by yellow sphere models) could play a role in generating activating effect. H163 and C25 constitute the active centre of cathepsin L. To show flexibility of the L2 loop, two conformations were superimposed based on their coordinates (1N5H and 1N5P, respectively. Green: cis; red: trans); (B) comparison of amino acid sequences of the CLD L2 loops between hCAP-18/LL37 and PG3. Identical residues in hCAP-18/LL37 are represented by dots. Seven deleted residues in PG3 CLD are underlined twice. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of the article.)