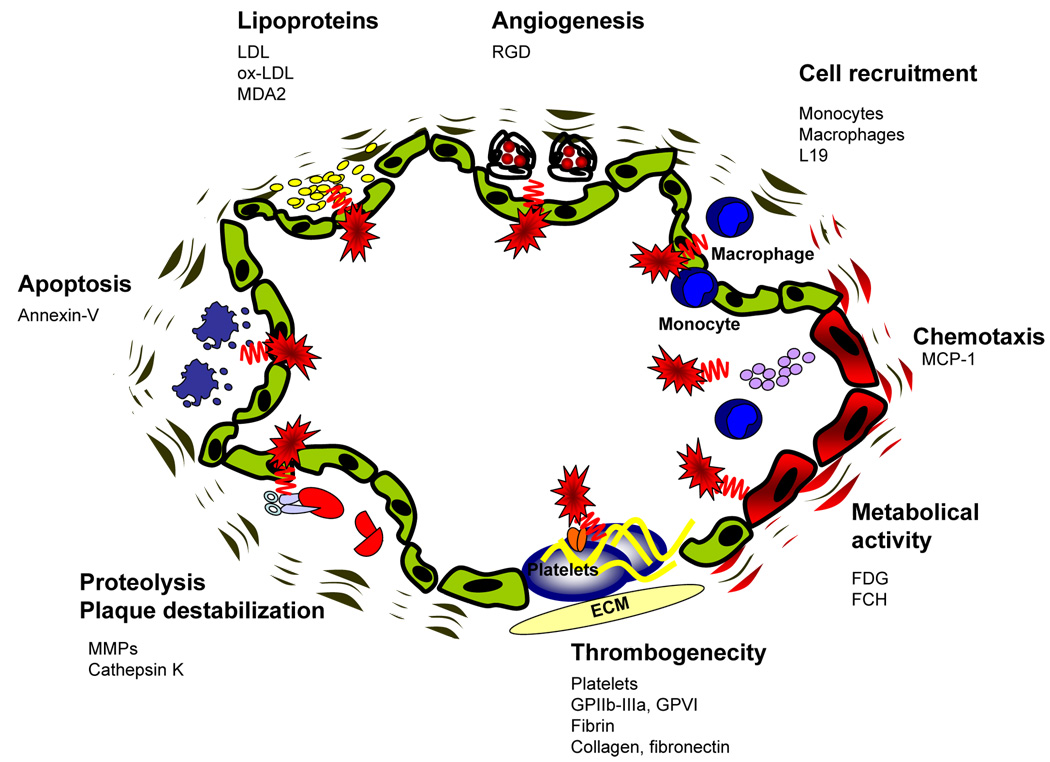
Fig 2. Molecular principles to detect atherosclerotic plaques.
Based upon the increasing molecular knowledge regarding atherogenesis, different principles have been successfully used to image atherosclerotic plaques. One major complex is the molecular imaging of inflammation, which includes enhanced metabolic activity, chemotaxis, cell recruitment and lipoprotein accumulation. Furthermore mediators of angiogenesis, apoptosis and matrix metalloproteinase activity have been successfully applied. Another promising approach to detect vulnerable atherosclerotic is the visualization of plaque thrombogenicity, including thrombosis and exposure of thrombogenic subendothelial matrix proteins. ECM = Extracellular matrix. GPIIbIIIa = Glycoprotein IIbIIIa. GPVI = Glycoprotein VI. FDG = fluorodeoxyglucose. MCP-1 = Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1. RGD = protein sequence "Arginine-Glycine- Aspartic acid". FCH = fluorocholine. LDL = low density lipoprotein. Ox-LDL = oxidized low density lipoprotein. MDA2 = malondialdehyde epitope on ox-LDL. MMPs = Matrix-Metalloproteinases. L19 = antibody against the extra-domain B of fibronectin.