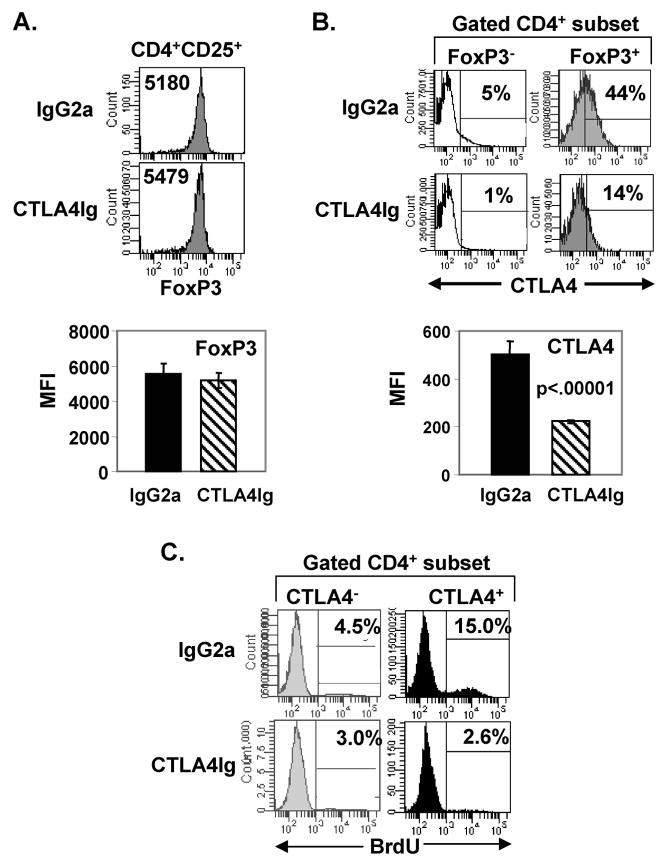
FIGURE 4. Inhibition of steady-state homeostasis selectively reduces CTLA4 expression on Tregs while FoxP3 expression is maintained.
BALB/c mice were treated with IgG2a or CTLA4Ig as in Fig. 3A, administered BrdU on days 4–6, and splenic CD4 T cells were harvested at day 7, and analyzed for FoxP3 and CTLA4 expression. (A) Comparable level of FoxP3 expression in IgG2a- and CTLA4Ig-treated mice. Top: Histograms show the level of FoxP3 expression of CD4+CD25+ T cells from IgG2a- and CTLA4Ig-treated mice, with MFI of FoxP3 indicated in each histogram. Bottom: Graph shows the average MFI of FoxP3 expression from 5 mice per group. Results are representative of 4 experiments. (B) CTLA4Ig treatment reduces CTLA4 expression on Tregs. Top: Histograms show CTLA4 expression gated on FoxP3+ and FoxP3− CD4 T cells from IgG2a- and CTLA4Ig-treated mice with the percentage CTLA4+ shown based on isotype control staining indicated by marker. Bottom: Graph shows average MFI of CTLA4 expression by FoxP3+ Tregs from IgG2a- and CTLA4Ig-treated mice (n=5 mice per group). Results are representative of 6 experiments. (C) Steady-state homeostasis of CTLA4+ and CTLA4− CD4 T cells in IgG2a- and CTLA4Ig-treated mice. Histograms show percent BrdU incorporation by CD4+CTLA4+ and CD4+CTLA4− T cells from total CD4 T cells in IgG2a- and CTLA4Ig-treated mice (n=5 mice per group).