Figure 1.
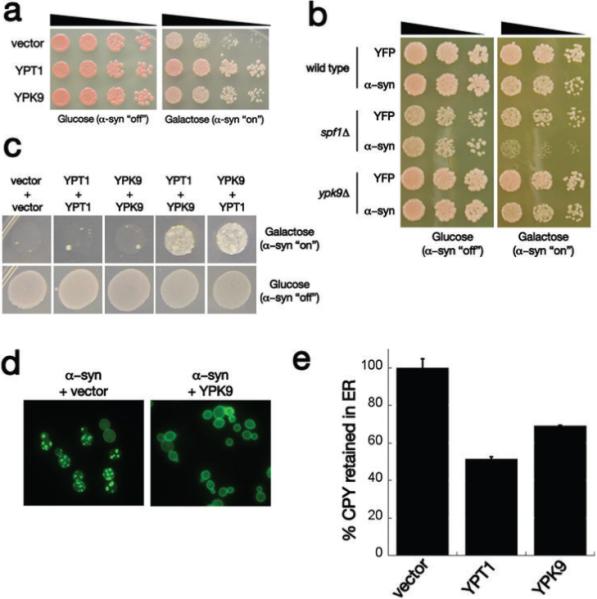
Interaction between 〈–syn and the yeast PARK9 homolog. a) Spotting assays with yeast 〈–syn toxicity modifier genes YPT1 and YPK9 showing their ability to suppress toxicity compared to empty vector control. Five-fold serial dilutions of yeast cells were spotted onto glucose (〈–syn expression repressed) or galactose (〈–syn expression induced). b) Deletion of Ypk9 has no effect on 〈–syn toxicity, however deleting the closely related ATPase Spf1 enhances 〈–syn toxicity. c) Synergistic genetic interaction between 〈–syn toxicity modifiers Ypt1 and Ypk9. In a high toxicity (HiTox) 2 copy 〈–syn yeast strain, expression of Ypt1 or Ypk9 alone is not sufficient to rescue toxicity. However, their co-expression restores growth to this strain. d) Ypk9 overexpression eliminates 〈–syn inclusions. 〈–Syn-YFP-expressing cells contain many vesicular inclusions when transformed with an empty vector and these are greatly diminished in cells transformed with a Ypk9 expression plasmid. e) The ability of Ypk9 to suppress the 〈–syn-induced block in ER-Golgi was measured by carboxypeptidase Y (CPY) maturation assay. Ypk9 significantly improved the trafficking of CPY from ER to Golgi.
