Figure 2.
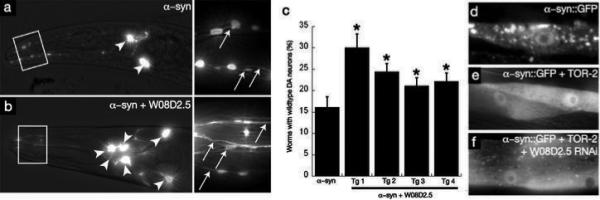
PARK9 antagonizes α–syn-mediated dopaminergic neuron degeneration in C. elegans. (a, b) Anterior DA neurons in worms expressing Pdat-1::GFP + Pdat-1::α–syn at the day 7 stage. Arrowheads and arrows depict cell bodies and neuronal processes, respectively. WT worms have 6 anterior DA neurons. a) α–Syn toxicity is depicted by the loss of anterior DA neurons. b) DA neurons are protected when Pdat-1::FLAG-W08D2.5 cDNA is co-expressed. c) Quantification of C. elegans PARK9 rescue of α–syn-induced neurodegeneration in 4 independent transgenic lines displaying all six anterior DA neuron. P < 0.05, Student's t test. d) Overexpression of α–syn in Punc-54::α–syn::GFP results in misfolding and aggregation of α–syn in body wall muscle cells at the young adult stage. e) Co-overexpression of TOR-2, a protein with chaperone activity, attenuates the misfolding of the α–syn::GFP protein. f) The misfolding of α–syn::GFP is enhanced following RNAi targeting W08D2.5.
